Big-O and Data Structures#
Each data structure we use as programmers has varying time and space complexities. As programmers we need to consider the programming problem and context we are working in, then choose appropriate data structures.
For data structures we can break down the time complexity based on the actions, which are:
Access - retrieve an element given a direct reference e.g. list index or key in a dictionary
Search - find an element based on a comparison e.g.
==`, ``>, or>=Insertion - adding a new element
Deletion - removing an element
Each data structure has strengths and weaknesses and we often need to make a tradeoff based on what actions we use. This is further complicated by the fact that most data structures have average and worst case complexities.
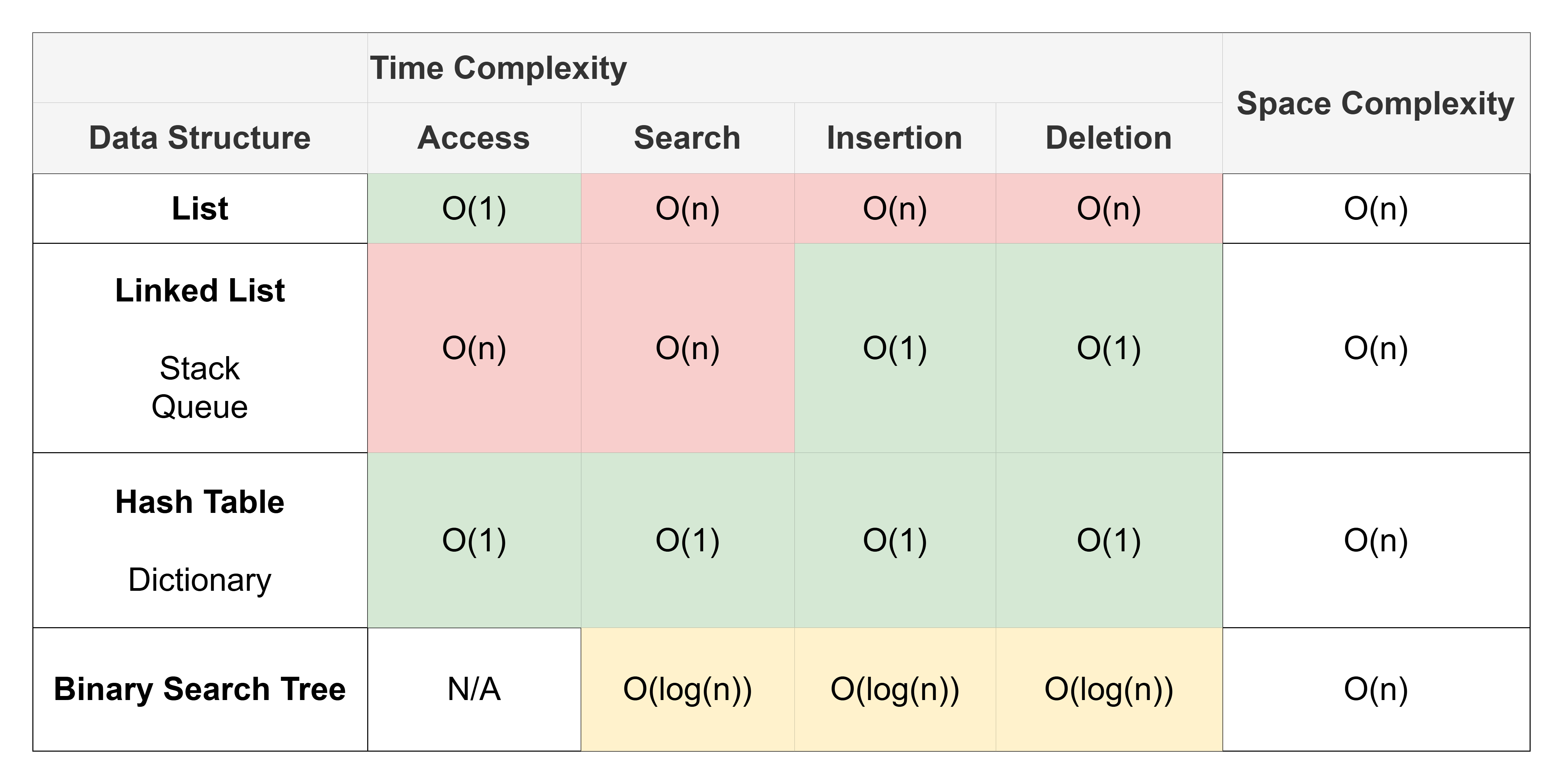
Average Complexities#
The table below shows the average complexities for each data structure. This means that given many of each operation we expect the following complexity.
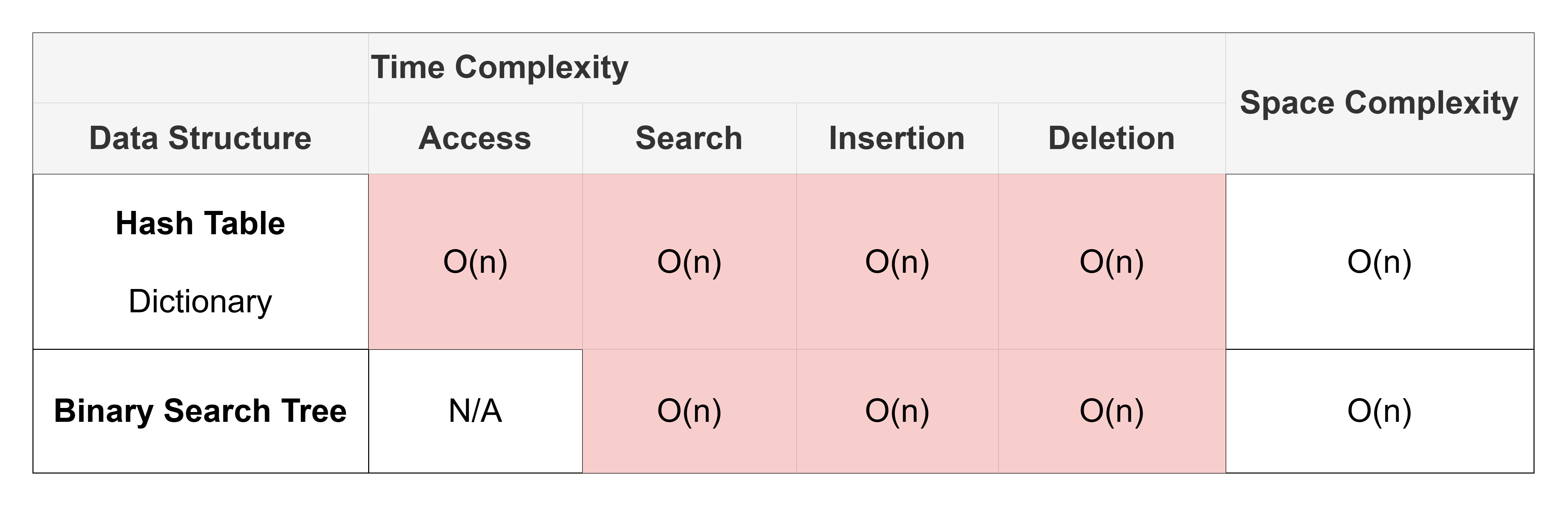
Worst Case Complexities#
The table below shows the worst case complexities. These are the complexities for specific situations of the data structures.
Notably, hash tables and binary search trees have \(O(n)\) worst case complexities for most actions. We’ll learn more about this later.