5.7. Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)#
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) is an attack where an attacker tricks a user into submitting unauthorised requests to websites where the user is logged in.
5.7.1. Recommended Video#
5.7.2. How CSRF Works#
A user logs in to a website, such as a banking application, and their browser stores a session cookie.
The user visits a separate, malicious website or clicks a deceptive link.
The malicious site or link causes the user’s browser to send a request to the banking application (for example, transferring money).
Because the user’s browser includes the valid session cookie, the banking application processes the request as though it were legitimate.
5.7.3. Example#
Suppose you run a website where users can posts short messages onto a public feed. To post messages, logged in users complete a form on your site that sends a POST request to your server.
An attacker could create a website that:
looks the same as yours (page styling and similar domain name)
contains a hidden form to post to your site
tries to submit the form, using the session cookie of the visiting user
With this technique, an attacker could post as any logged in user that visits the malicious site that they set up.
5.7.4. Preventing XSS#
There are two main techniques to preventing XSS attacks.
CSRF Tokens
A CSRF Token is a unique identifier that the webserver inserts onto its own pages. This token is attached to any forms that are submitted from these pages.
If the web server receives a request with form data it checks for the presence and correctness of the token. If the token is missing or incorrect then the request is rejected.
SameSite Cookies
By setting cookies with SameSite=Lax or SameSite=Strict, browsers will
not include those cookies on cross-site requests. In other words the cookies
are only sent when the browser is on a page that created them.
Demo: CSRF Demo
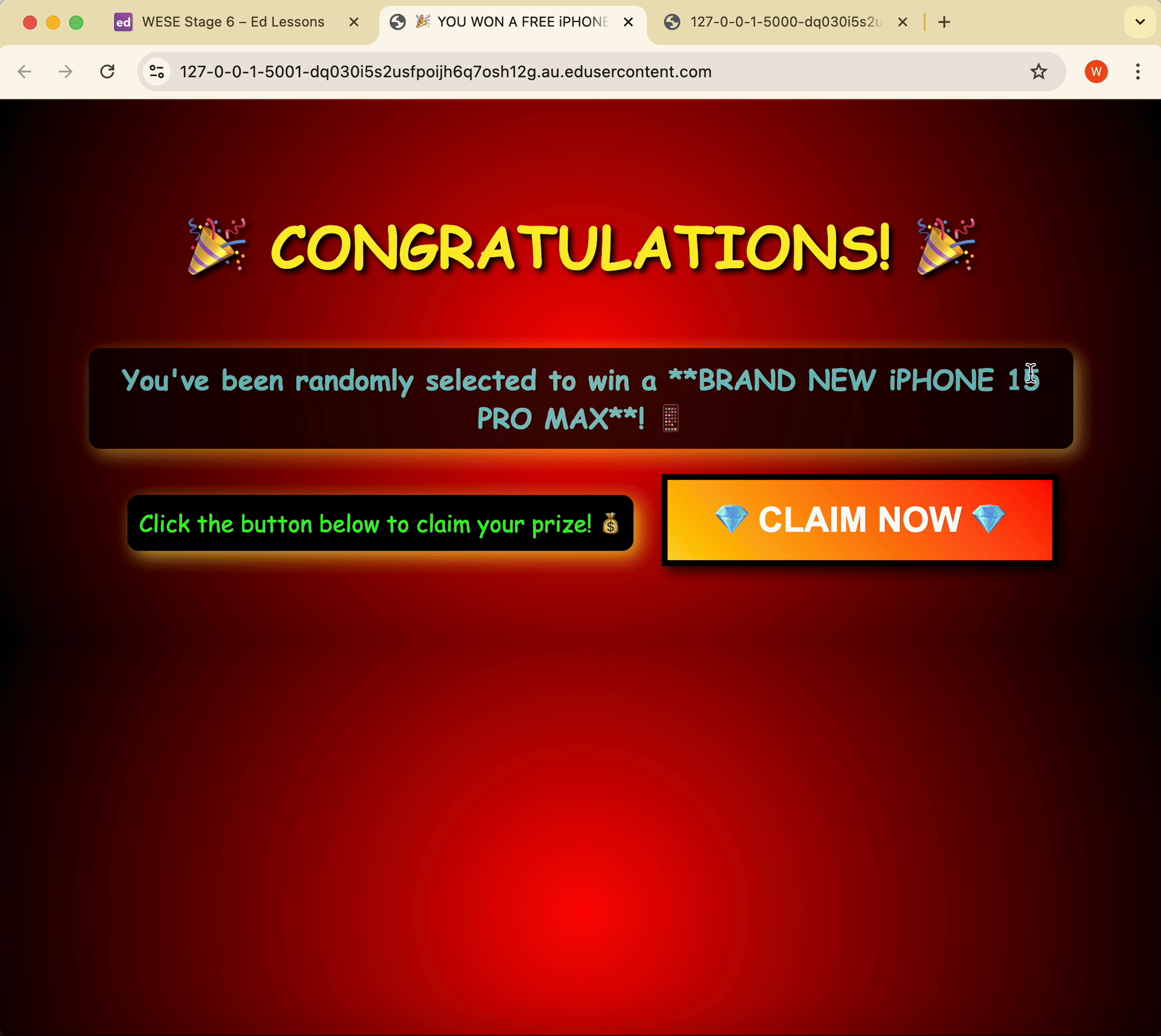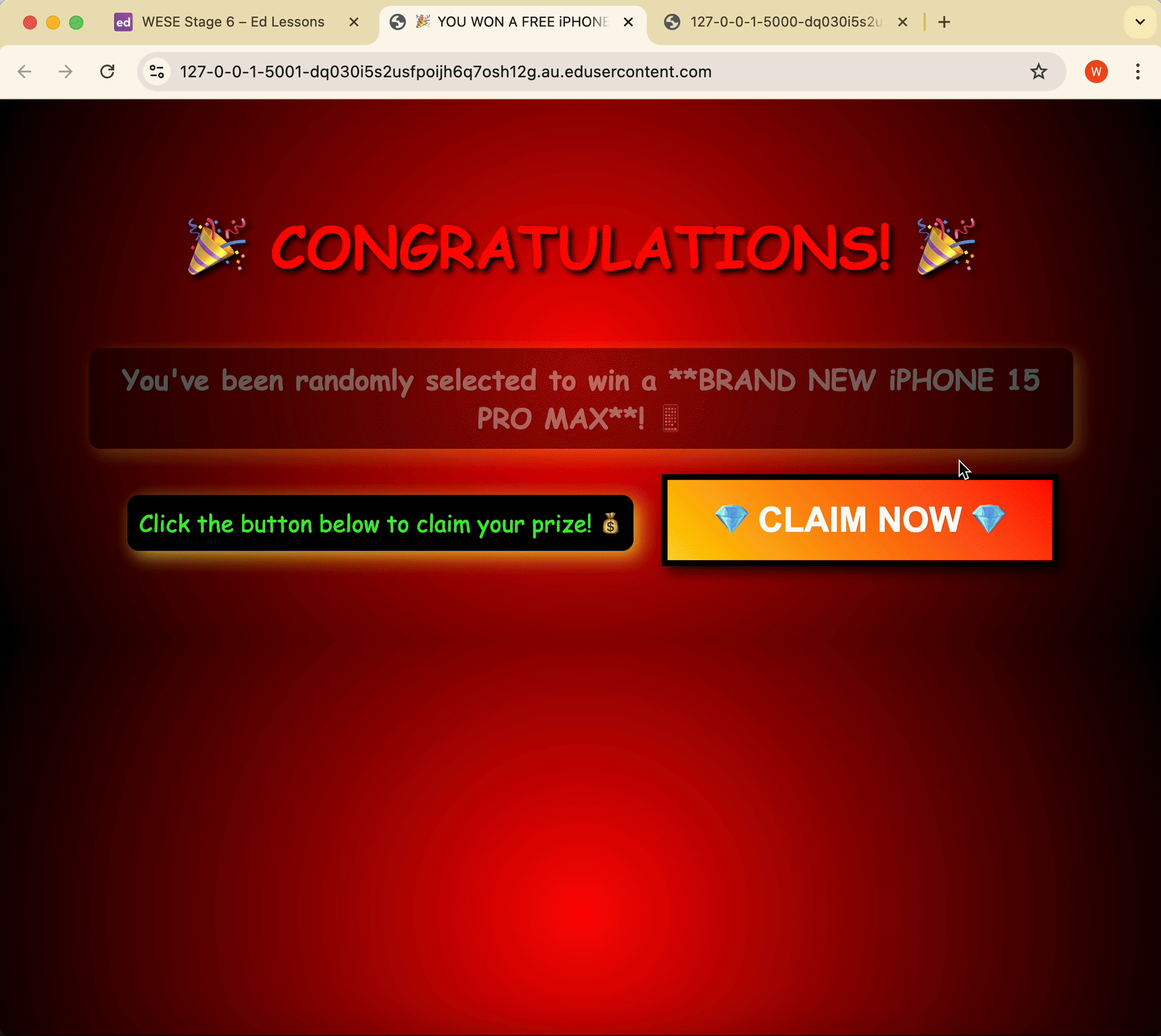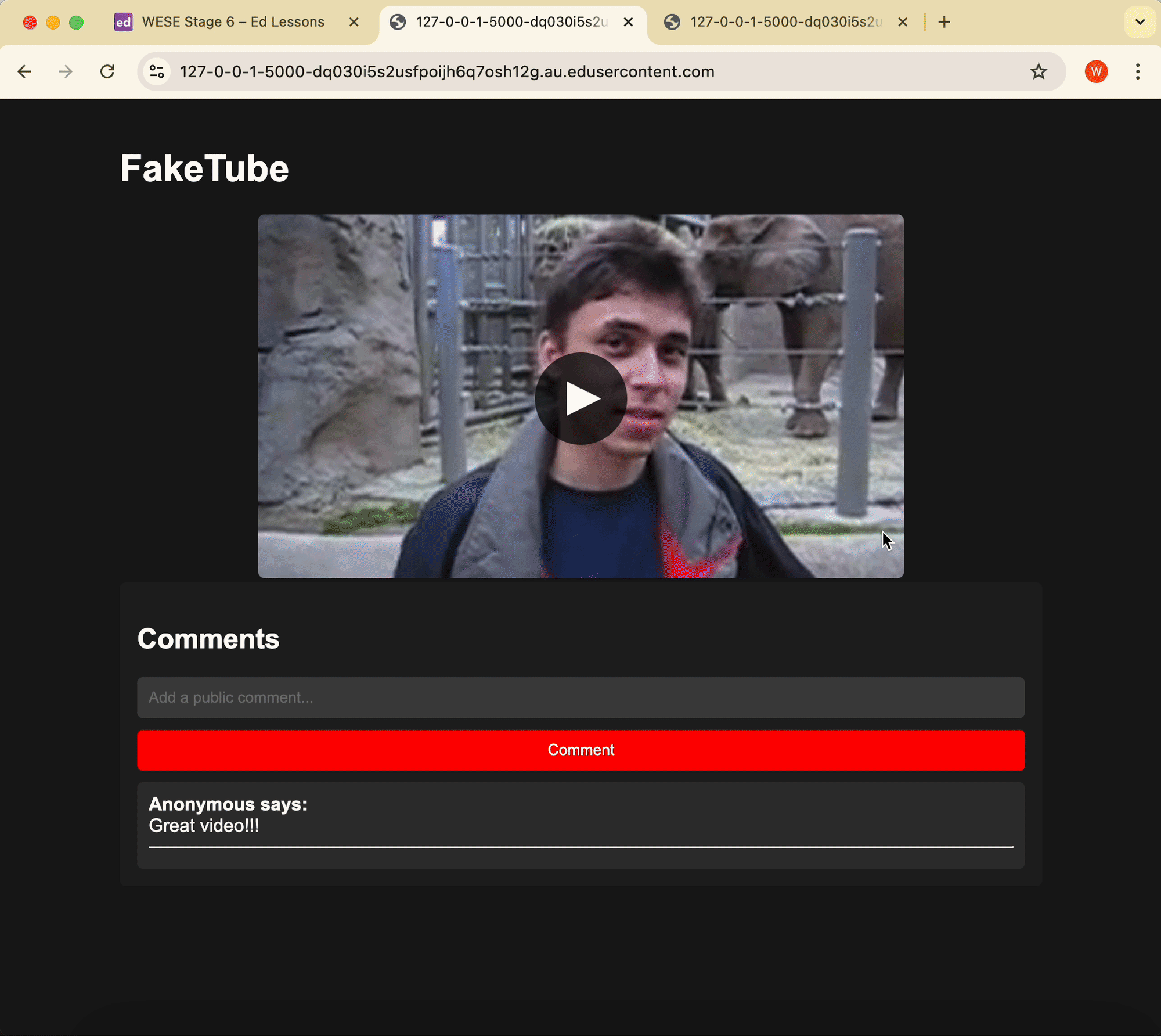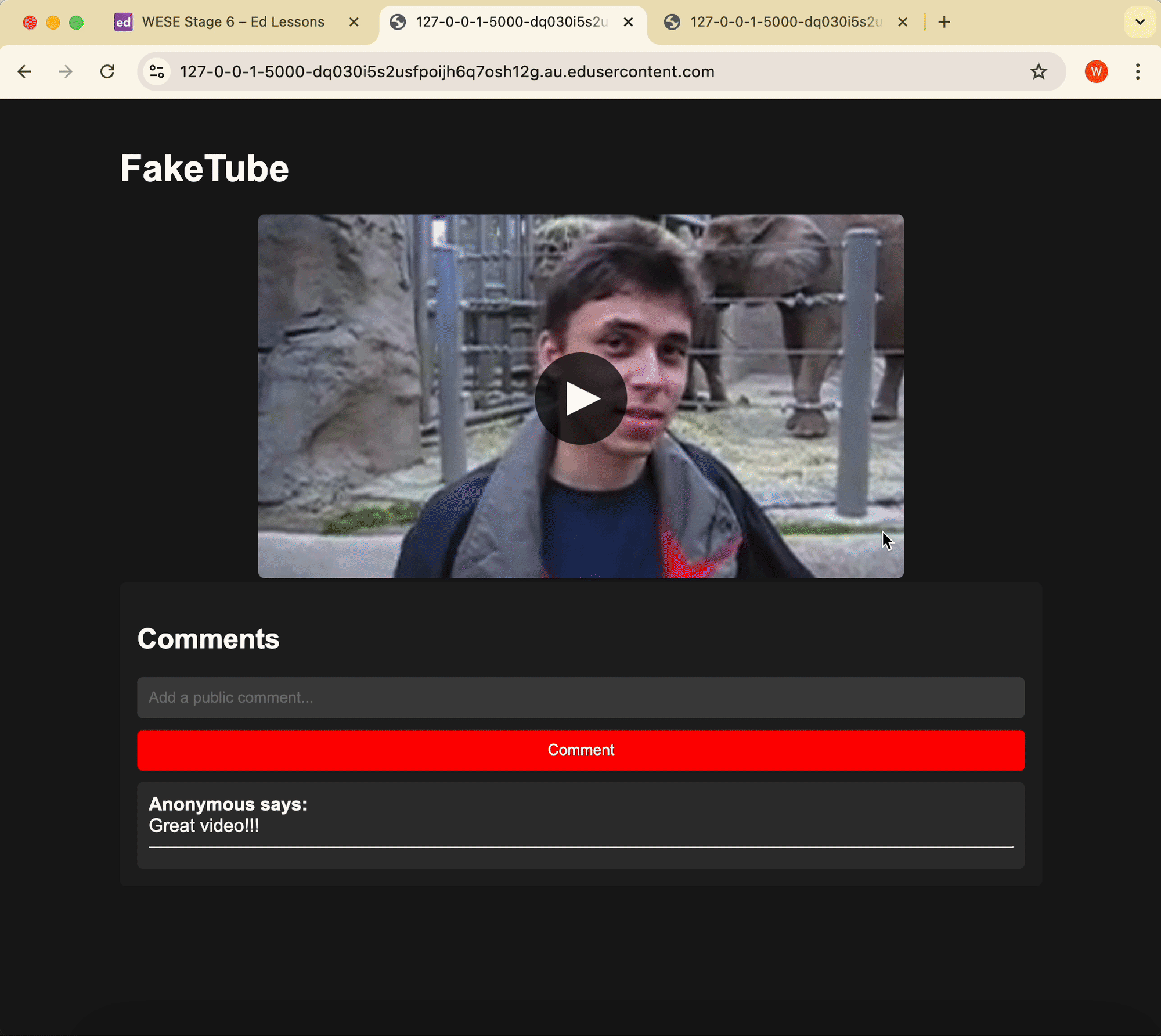
The uploader of the video on FakeTube is trying to increase the number of comments on his video. He’s setup a fake website offering free iPhones if users click a button.
Unbeknownst to the user, clicking the button posts a comment on his video, from the user’s browser.
The uploader is using CSRF to boost the number of comments on the video!
Instructions
Run the FakeTube app
python app.py
Then open the site in your browser.
Run the scam comment app (at the same time)
python scam_app.py
Then open the site in your browser.
Click to claim your free iPhones
Congrats, you’ve been tricked into posting on the video!
Note
When you click ‘CLAIM NOW’, the comment ‘Great video!!!’ is posted to the video.