2.2. Ciphers#
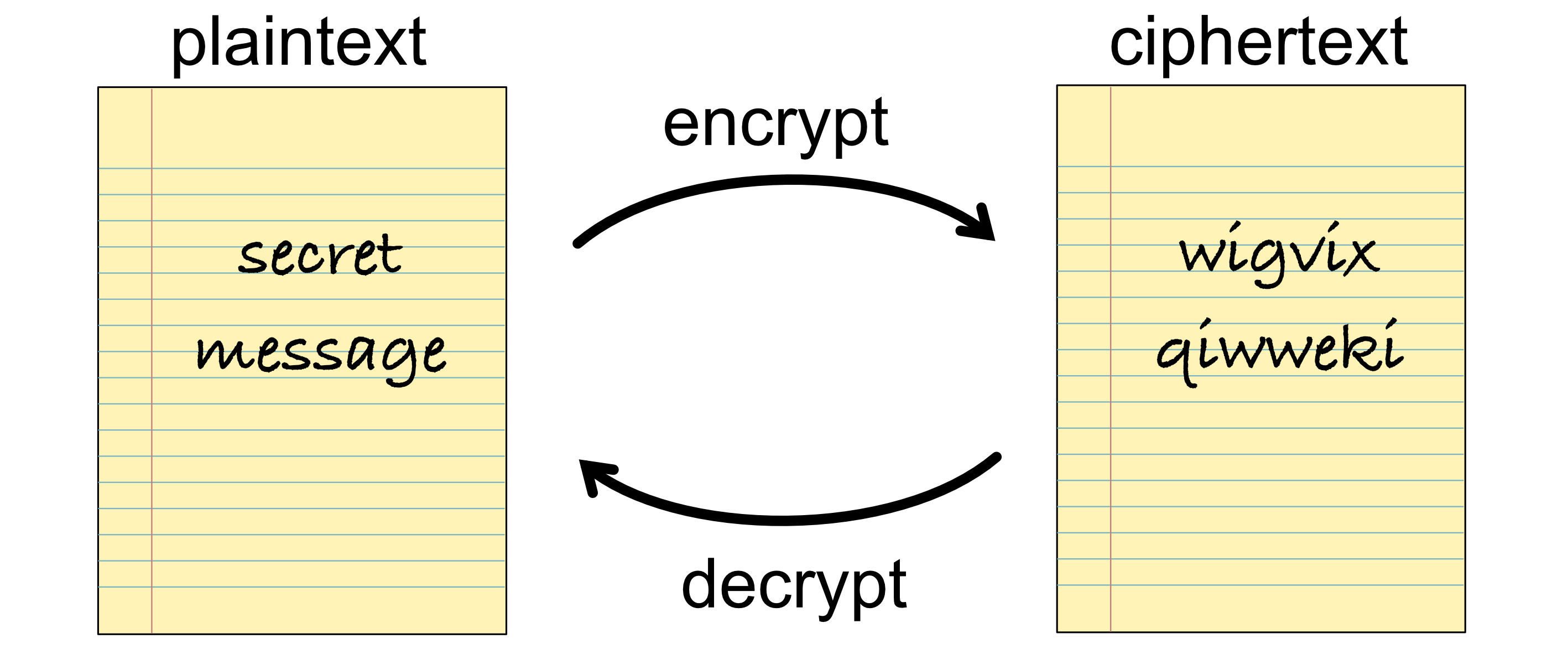
Ciphers are a fundamental part of cryptography, serving as the method used to transform readable information, called plaintext, into obscured data, called ciphertext. By applying specific steps, usually mathematical operations, ciphers convert potentially sensitive information into a form that can only be understood by those who have knowledge on how to reverse it.
The primary purpose of a cipher is to secure information against unauthorised access. Whether we are protecting online transactions, guarding personal communications, or shielding government intelligence, ciphers ensure that data remains private.
The process of applying a cipher to plain text is called encryption. The reverse process, converting cipher text to plain text, is called decryption. The decryption process requires knowledge of the cipher and often additional information such as a key.
2.2.1. Using Ciphers#
Write your data in plaintext. It could be a message, a document, or any data that needs protection.
Encrypt the plain text. Using a specific cipher and an associated key, the plain text is scrambled.
Store or send the ciphertext.
Decrypt the cipher text. The recipient applies the method and/or key used to encrypt the data. This reverses the encryption process and retrieves the original plain text.
2.2.2. Types of Ciphers#
In this module, we will learn about the following types of ciphers.
Substitution Ciphers
Modern Cryptographic Ciphers