Inheritance#
Inheritance#
Inheritance allows us to define classes based on other classes.
A child class is a class that inherits the attributes and methods of a parent class.
Child classes can extend and modify the attributes and methods of a parent class.
Generalisation#
The concept of collecting shared attributes and methods into a common parent class is called generalisation. This is what allows us to avoid repeating the same code for multiple classes. It also can make our code easier to read and understand by eliminating redundant code.
Creating a child class that extends or modifies a parent class is called specialisation.
Terminology#
There is various terminology used to describe parent and child classes. The list below serves to introduce the different terminology used and you may find that we interchange terminology in this section:
Parent classes are also known as “super” or “base” classes
Child classes are also known as “sub”, “derived” or “extended” classes
Syntax#
To specify the class to inherit from we modify the class name definition to:
class ChildClassName(ParentClassName):
where
ChildClassNameis the name of the class you are definingParentClassNameis the parent class you want to inherit fromThe
( )separate the names
With two classes the syntax looks like:
class ParentClassName:
def __init__(self, parameter_1, ..., parameter_n):
# Set values here
class ChildClassName(ParentClassName):
def __init__(self, parameter_1, ..., parameter_n):
# Set values here
Example
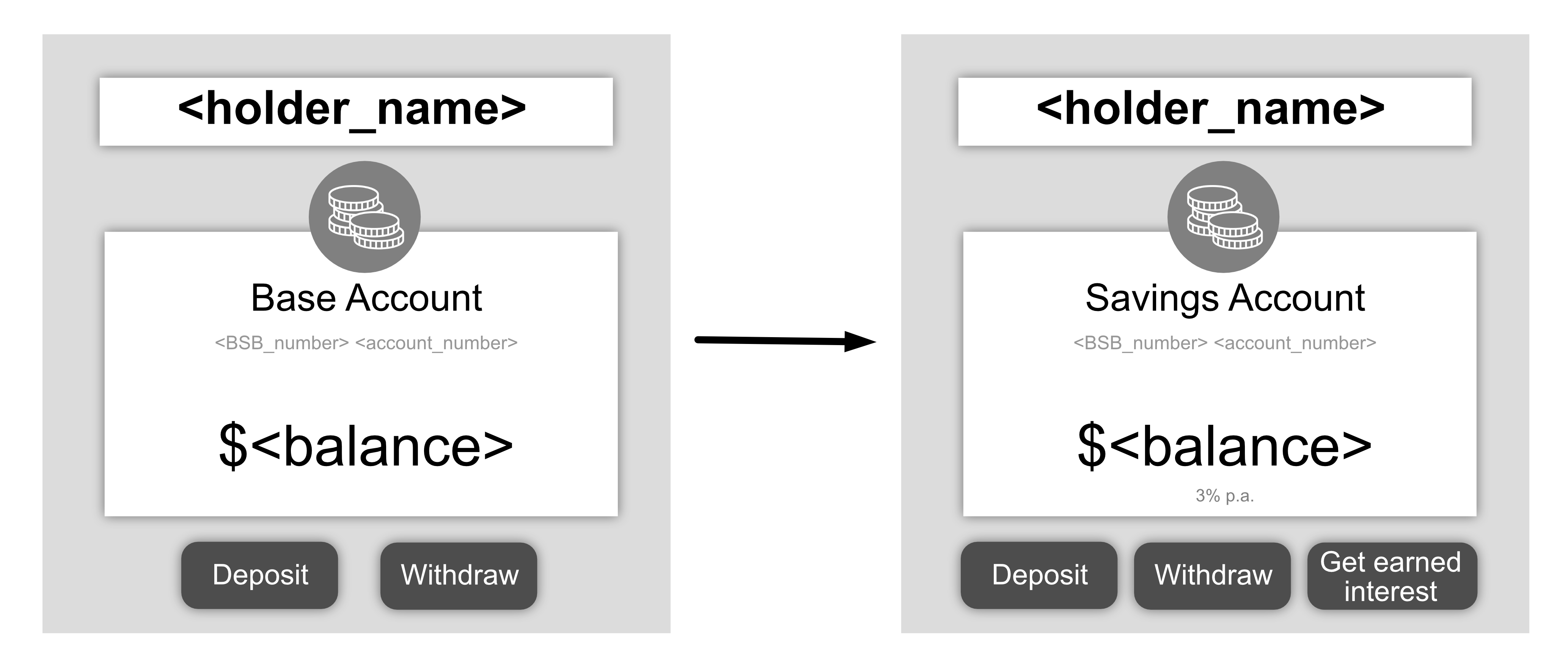
In the example below the SavingsAccount class inherits from the BaseAccount
class BaseAccount:
def __init__(self, account_number, balance, holder_name):
self.account_number = account_number
self.balance = balance
self.holder_name = holder_name
def deposit(self, amount):
self.balance += amount
def withdraw(self, amount):
self.balance -= amount
class SavingsAccount(BaseAccount):
interest_rate = 0.03 # 3% interest rate
def get_earned_interest(self):
return SavingsAccount.interest_rate * self.balance
Rules to Know#
If a child class does not define its own constructor,
__init__, the parent class’s constructor is used.If a child class defines its own constructor, it must initialise any attributes used by the parent class.
A child class automatically inherits methods from its parent class.
A child class can define a method with the same name as one in the parent class. This is called overriding. When this happens, the child’s version replaces the parent’s version for instances of the child class.