4.11. Extension: Image Data#
Here we’ll look at how black and white images can be represented as an array of numbers. Consider the following image of a tree.
We can take this image an ‘unwrap’ it into one long row of pixels.
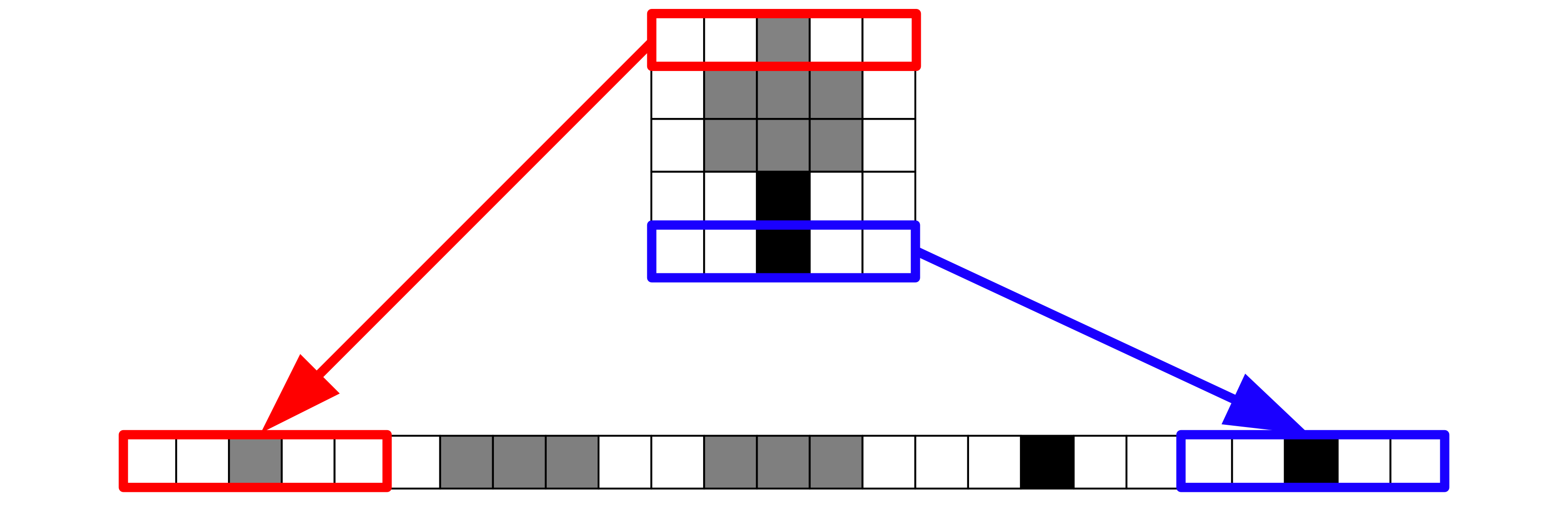
From here, we assign the colour of each pixel a number based on the shade. 0 means the pixel is white, black means the pixel is black and numbers in between are shades of grey.
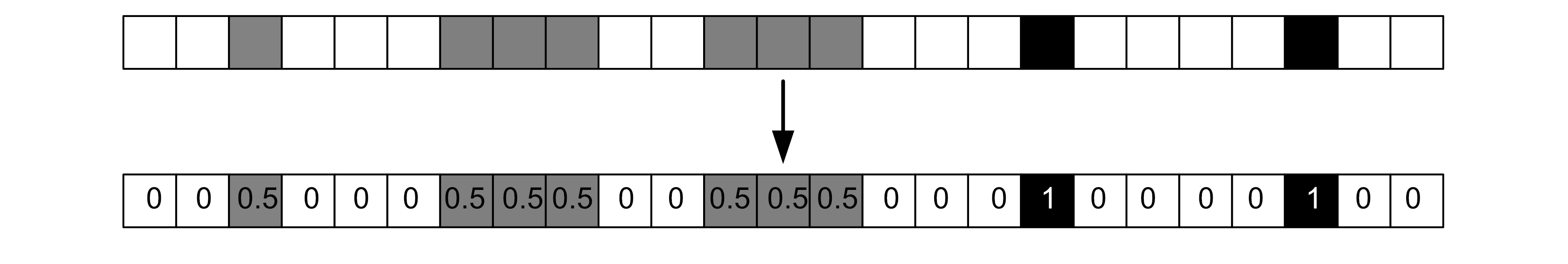
We then store these values as an array.
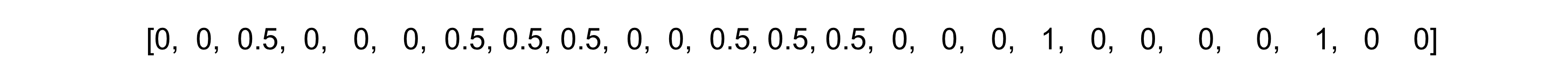
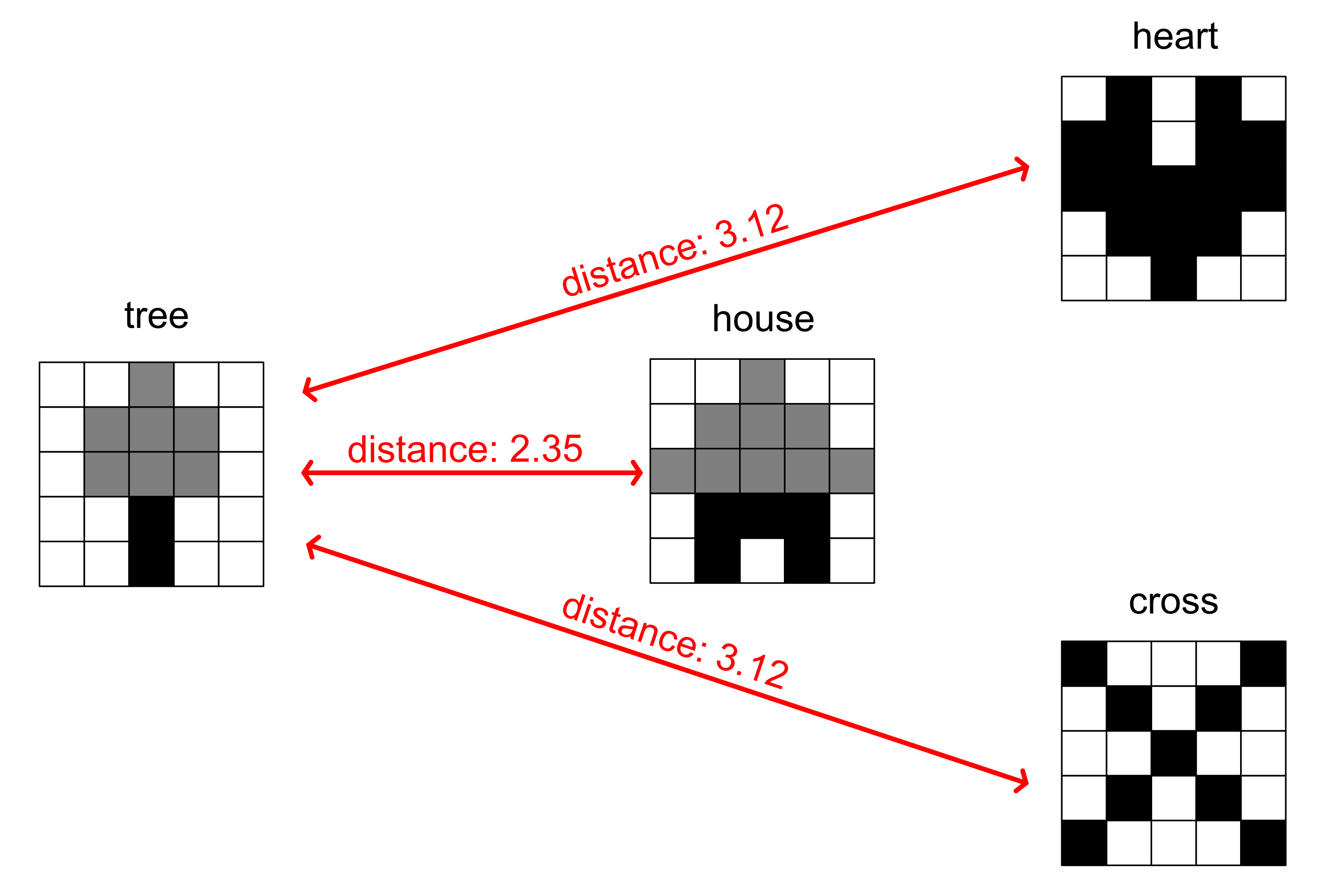
Now consider the following three images.
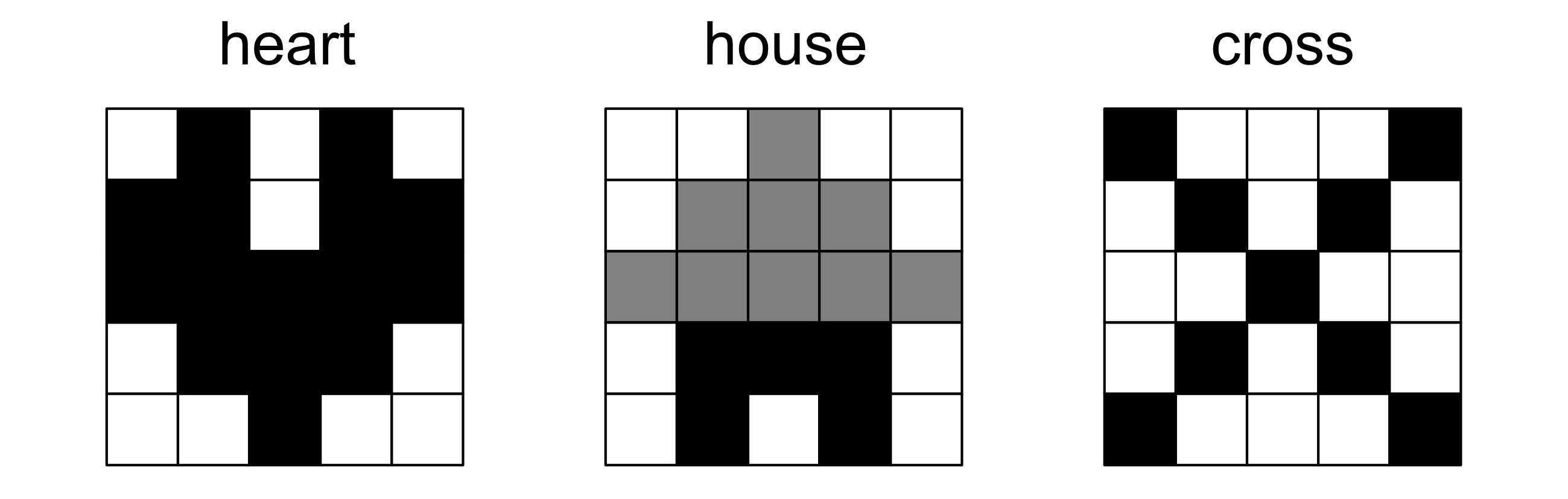
Here are the array representations of these images.
import numpy as np
heart = np.array(
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0]
)
house = np.array(
[
0,
0,
0.5,
0,
0,
0,
0.5,
0.5,
0.5,
0,
0.5,
0.5,
0.5,
0.5,
0.5,
0,
1,
1,
1,
0,
0,
1,
0,
1,
0,
]
)
cross = np.array(
[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1]
)
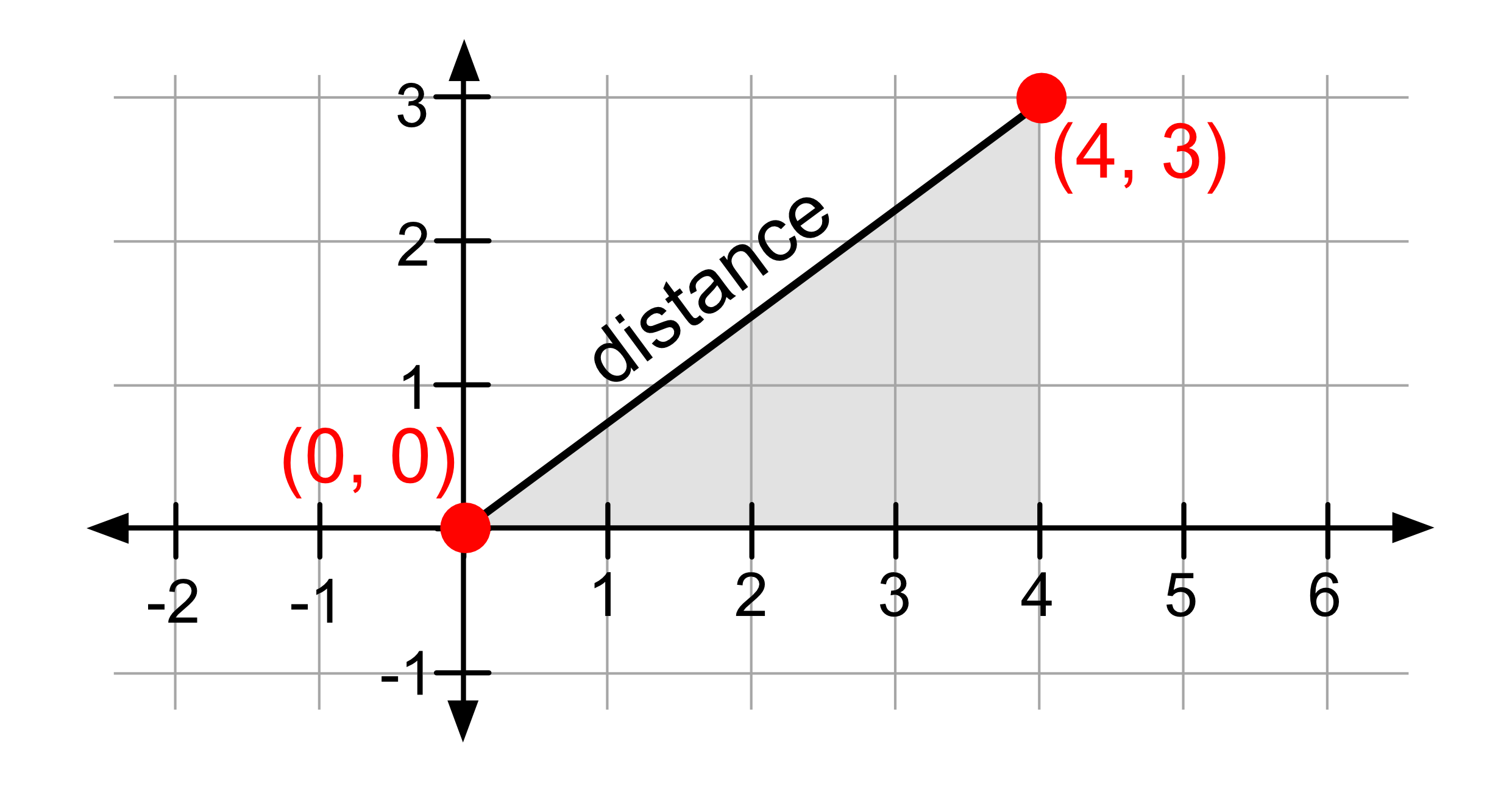
We can calculate the distance between arrays using math.dist. Here’s a quick example of how it works.
import numpy as np
import math
x = np.array([0, 0])
y = np.array([4, 3])
print(math.dist(x, y))
Output
5.0
We see that the distance between the points (0, 0) and (4, 3) is 5. We can also verify this using Pythagoras’ Theorem. Recall that \(a^2 + b^2 = c^2\), in this case the length of the hypotenuse \(\sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} = \sqrt{25} = 5\).
We can use this same function to calculate the distance between our original tree image and each of our three new images.
import numpy as np
import math
tree = np.array(
[
0,
0,
0.5,
0,
0,
0,
0.5,
0.5,
0.5,
0,
0,
0.5,
0.5,
0.5,
0,
0,
0,
1,
0,
0,
0,
0,
1,
0,
0,
]
)
heart = np.array(
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0]
)
house = np.array(
[
0,
0,
0.5,
0,
0,
0,
0.5,
0.5,
0.5,
0,
0.5,
0.5,
0.5,
0.5,
0.5,
0,
1,
1,
1,
0,
0,
1,
0,
1,
0,
]
)
cross = np.array(
[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1]
)
print("Tree to heart: {:.2f}".format(math.dist(tree, heart)))
print("Tree to house: {:.2f}".format(math.dist(tree, house)))
print("Tree to cross: {:.2f}".format(math.dist(tree, cross)))
Output
Tree to heart: 3.12
Tree to house: 2.35
Tree to cross: 3.12
You’ll see that the tree is closest in distance to the house. And intuitively this should make sense because the house image is most similar to the tree image, and as we have previously discussed, distance can be used as a measure of similarity.