7.4. MLOps#
7.4.1. What is MLOps?#
From HSC Course Specifications:
MLOps is the automated process of designing, training and deploying machine learning models. It borrows many of the same principles and practices used in DevOps, bringing together the teams involved in developing machine learning models and the operational teams involved in deploying and supporting the models in production.
Recommended Video: What Is MLOps? (6 mins)
7.4.2. MLOps Stages#
The MLOps process can be represented in multiple ways. The following diagram breaks the MLOps down into eight stages.
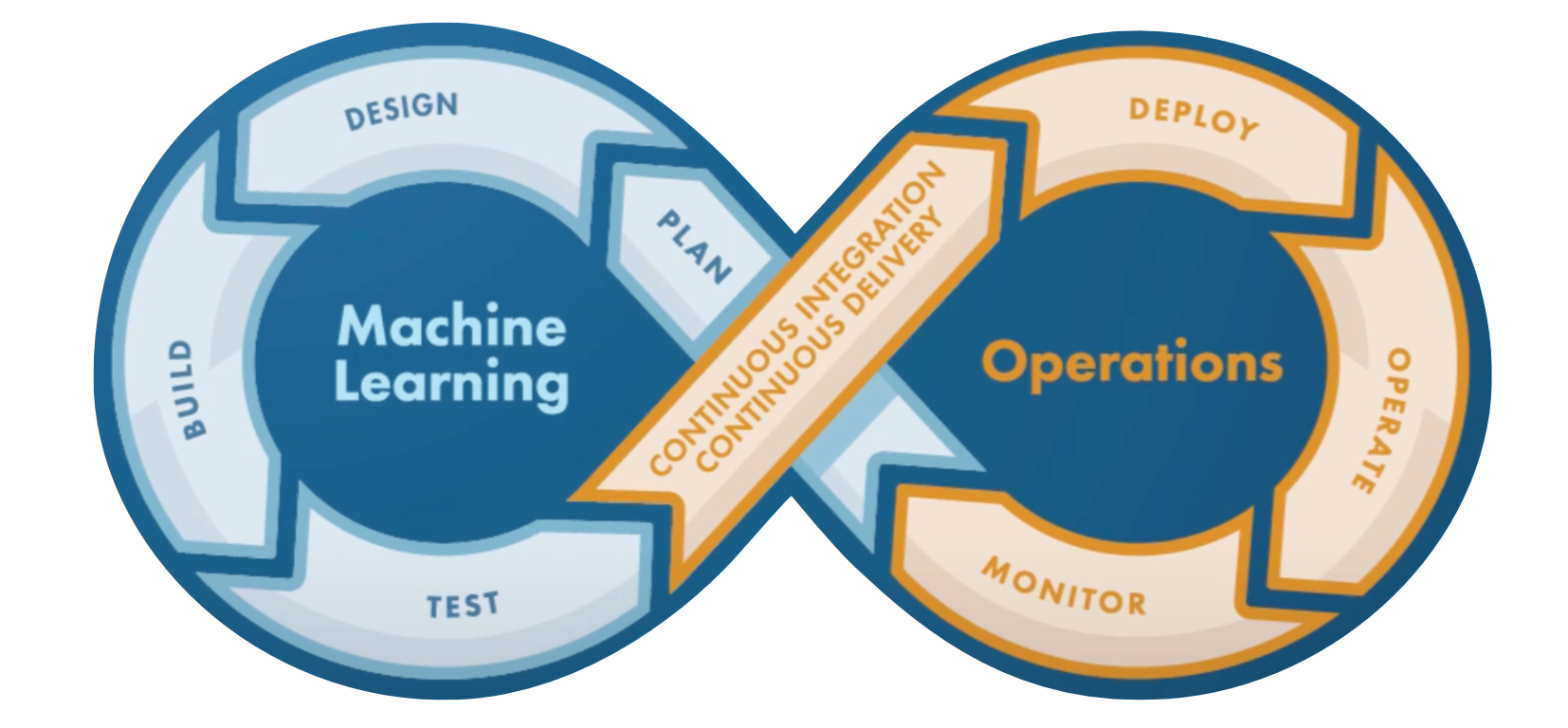
Whereas the HSC Course Specifications breaks the process down into three stages.
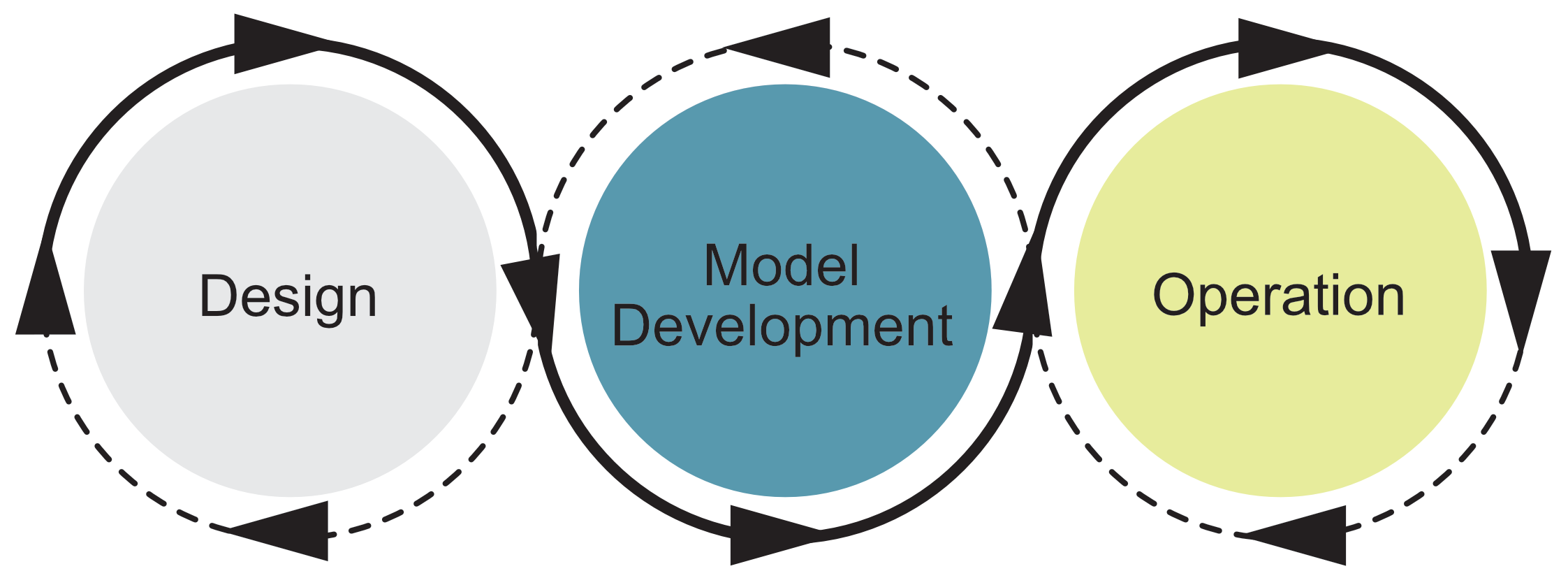
The loop structure in both diagrams highlights the continuous and iterative nature of the MLOps processes. It shows that building and maintaining ML systems is not a one-time effort but an ongoing cycle of improvement. As data changes or new insights emerge, models must be updated and refined. Feedback from deployment and operation stages is used to inform future design and development decisions. Regular testing, monitoring, and retraining ensure that the system remains accurate, relevant, and effective over time. This cyclical approach supports long-term reliability and adaptability in real-world applications.
7.4.3. The 3-Stage Diagram#
We will focus on the 3-Stage diagram because this is the version used in the HSC Course Specifications.
Design#
This is the planning and preparation stage where the business problem is identified, project goals are set, and key decisions are made regarding the data to be used and the choice of machine learning algorithm. This phase includes:
Selecting data sources
Choosing evaluation metrics
Designing the machine learning model
Planning for ethical considerations, fairness, and explainability
Model Development#
This is where data scientists build, train, and validate machine learning models. This includes:
Data cleaning and pre-processing
Feature engineering (selecting which variables to use or creating new variables)
Training the model
Tuning hyperparameters with validation data
Evaluating the model performance with test data
Operation#
This involves deploying the model into a production environment and ensuring it performs well over time. This includes:
Model deployment
Supporting operation/use and managing infrastructure to ensure scalability
Monitoring model performance and detecting model drift