Nodes#
To implement the data structures we’ve introduced such as linked lists and hash
tables we will use a common base class to hold each element of data. We call
this common object a Node.
The Node class:
holds the associated data in an attribute called
dataholds the next node in an attribute called
next(defaults toNone)implements the
__str__method, which returns the string representation of the data
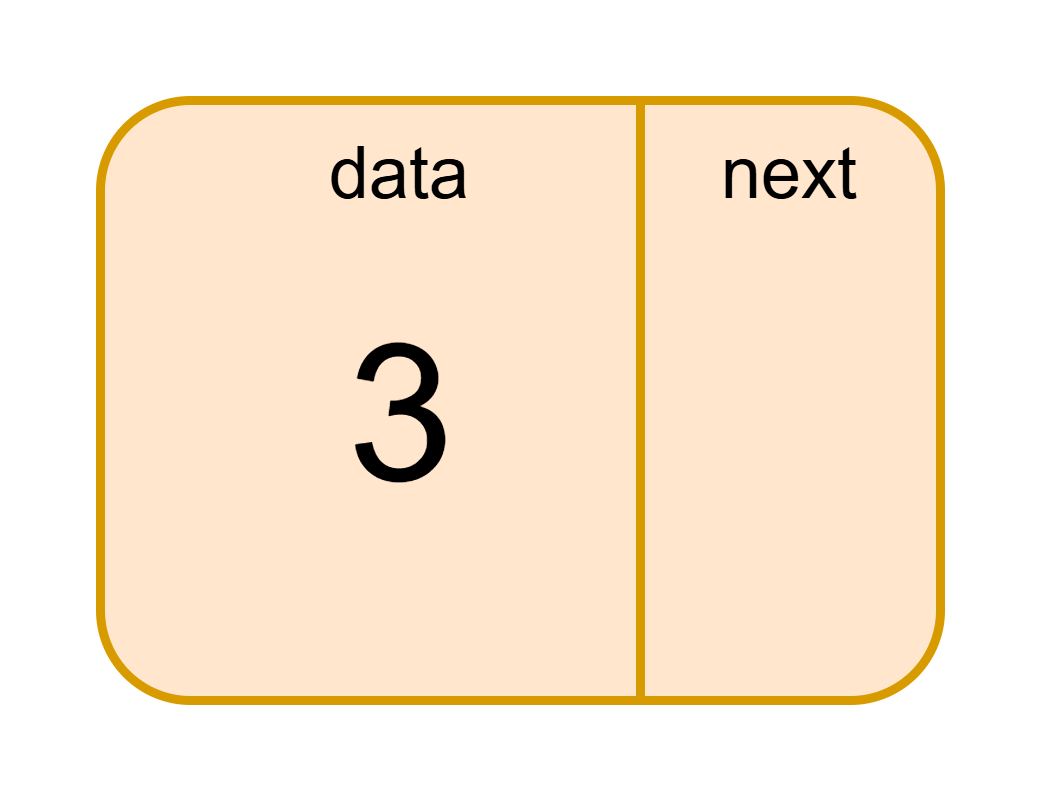
Example: single node
>>> node = Node("hello", None)
>>> print(node)
hello
Example: linking nodes
>>> node2 = Node("Bill Gates", None)
>>> node = Node("Steve Jobs", node2)
>>> print(node.next)
Bill Gates
example.py#
class Node:
def __init__(self, data, next=None):
self.data = data
self.next = next
def __str__(self):
return str(self.data)
# Test code
node3 = Node("Albanese")
node2 = Node("Morrison", node3)
node1 = Node("Turnbull", node2)
print(node2.next)
Output
Albanese