4.2. Password Authentication#
Password authentication is one of the most common ways websites verify user identities. When a user logs into a website, the server checks if the username and password match a stored user record. If they do, the user is granted access.
To implement password authentication, a web application must:
Store user records, including usernames and passwords.
Provide a way for users to register an account.
Allow users to log in by entering their username and password.
Verify that the provided credentials match the stored user data.
4.2.1. Storing User Records#
A web application needs a database to store user records. Each user record typically includes:
A unique username (or email) that identifies the user.
A password that the user chooses when registering.
Additional user details, such as full name, email, and role (e.g., student, teacher, admin).
A simplified user database table might look like this:
User ID |
Username |
Password |
|---|---|---|
1 |
alice123 |
mypassword123 |
2 |
bob_smith |
securepass456 |
3 |
admin |
superadmin789 |
Warning
⚠️ Important: In a real application, passwords should never be stored in plain text (we will cover secure password storage in a later section).
User Registration#
Before a user can log in, they need an account. There are two ways accounts can be created:
Self-Registration
Most websites allow users to create their own accounts. This process typically involves:
The user visits a Sign Up page.
They enter their username, email, and password.
They submit the form.
The system checks if the username is already taken.
If the username is unique, the system saves the new user record.
The user is now registered and can log in.
Admin-Created Accounts
In some cases, an administrator creates accounts for users. This is common in restricted platforms where approval is required before a user can access the system. Some examples:
Schools: A teacher or IT staff creates student accounts.
Workplaces: A company IT department sets up employee accounts.
The process typically involves:
The admin creates a new user account in the system.
The system generates a temporary password for the user.
The user receives login details via email or another method.
The user logs in and may be required to set a new password.
Login Process#
Once a user is registered, they can log in by following these steps:
The user enters their username and password on the login page.
The system searches for a matching username in the database.
If the username exists, the system checks if the password matches.
If the password is correct, the user is authenticated and granted access.
If the password is incorrect, the system denies access and may display an error message.
What Happens After Login?
If authentication is successful, the system creates a user session so the user remains logged in. We will discuss this in a layer section.
Code Challenge: Users from Scratch
Implement a simple login page. The page should only allow users to log in with the following credentials:
username: admin
password: password123

You have been provided with a scaffold with a simple database using Object Relational Mapping (ORMs covered in Programming for the Web > Object-Relational Mapping > Tutorial: ORMs in Flask). This database, instance/users.db contains user information but in this example it only contains a record for one user.
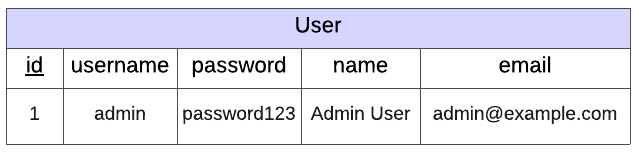
Warning
Do not edit this database. If you accidentally delete the database or edit it then run python make_db.py to restore it.
You have also been provided with the following html templates (do not edit these templates):
login.htmlsuccess.html
Instructions
You should only edit the home_post() function in app.py
Get the
usernameandpasswordfrom the form data
username = request.form['username']
password = request.form['password']
Query the
Usertable to see if a user exists with the given username and password
user = User.query.filter(User.username==username, User.password==password).first()
2.1 If a user exists with the given credentials, this user will be returned. In this case render the success.html template providing user information
return render_template('success.html', user=user)
2.2 If a user doesn’t exist with the given credentials the query will return None. In this case render the login.html template providing error="Invalid username or password" (templating covered in Programming for the Web > Dynamic Backend: Templates > Templates in Flask)
return render_template('login.html', error="Invalid username or password")
Download the scaffold and write your code in app.py.
SCAFFOLD_users_from_scratch.zip
Solution
Solution is locked