3.2. Digital Signatures#
Digital signatures are a way to ensure authenticity in digital communications. Just like a handwritten signature verifies the authenticity of a physical document, a digital signature proves that a message or file was created by a specific sender.
Digital signatures rely on asymmetric encryption, with the private key used to sign a message, and the public key is used to verify the signature.
3.2.1. Signing#
To create a digital signature, the sender:
Hashes the message, using a cryptographic hash function e.g. SHA-256
Encrypts the hash, using the sender’s private key to create the signature.
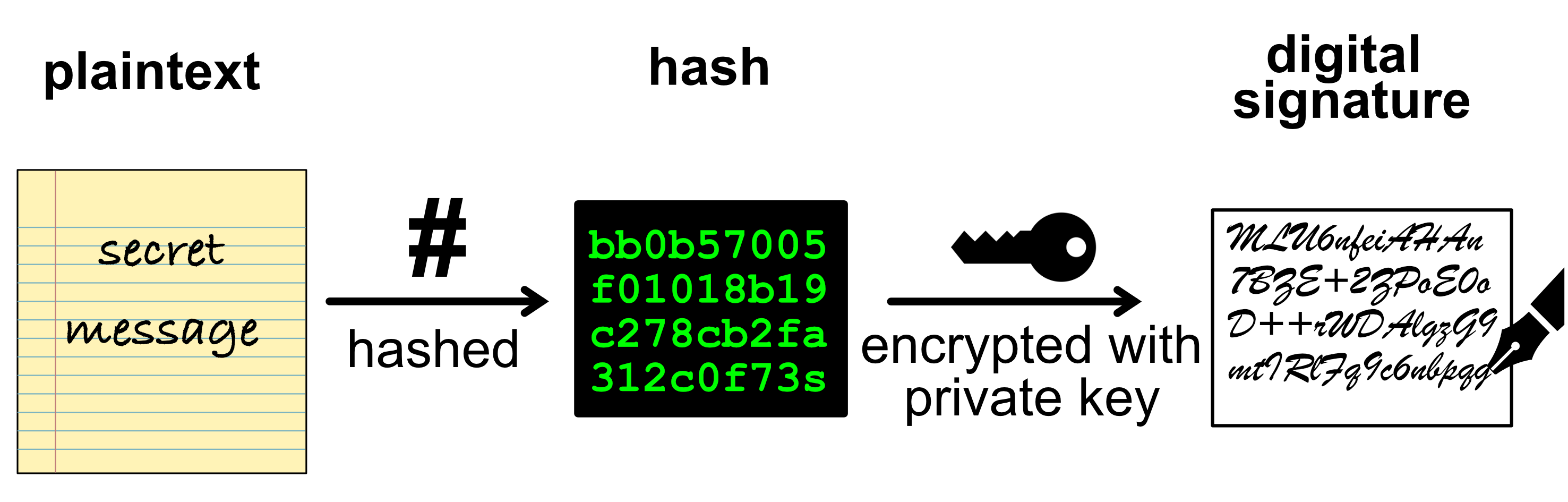
The sender then sends both:
The original message
The signature.
3.2.2. Verifying#
To verify a digital signature, the receiver:
Hashes the message, using the same hash function as the sender.
Decrypts the signature, using the sender’s public key into the decrypted hash.
Compares the hash of the message with the hash from the signature.
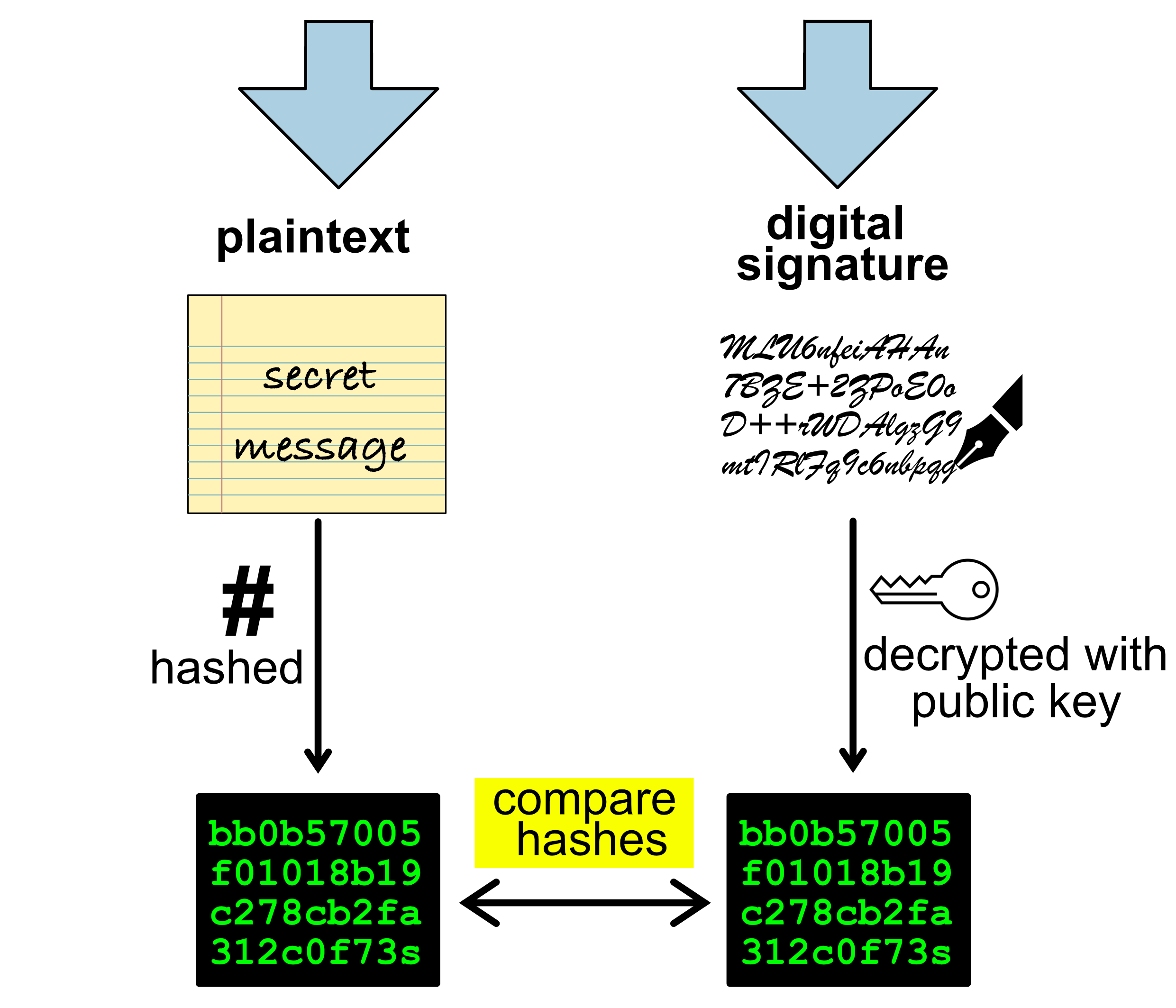
If the two hashes match then the signature is valid and it is confirmed that the sender was the creator of the message.
Otherwise the signature is invalid and we cannot confirm that the sender was the creator of the message.
3.2.3. Why Sign the Hash?#
Signing the hash is required because asymmetric encryption can only be applied to as many bits as used for the key. For example if using RSA with a 256 bit key we can only encrypt 256 bits of data. This means that we cannot sign arbitrarily long data.
To get around this, we sign the hash, which uniquely identifies the data regardless of how many bits it occupies.
Signing the hash also provides benefits:
Efficiency
Compared with signing the entire contents of a message:
it is much faster to encrypt a relatively short hash
it reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over a network
Integrity
Since any change in the message changes the hash it means that we can also verify the integrity of the message. In other words it also confirms that the message was not corrupted or tampered with.
3.2.4. Recommended Video#
Demo: Crypto Module - Signing
We’ve provided you with an updated crypto module that also that adds the following methods to the Asymmetric class:
sign- used to create a signature for a hash valueverify- used to get the hash value from a signature and public key
This page serves to explain how to use these new methods.
Signing
The static method Asymmetric.sign(message, private_key):
accepts two parameters:
messagewhich is thestrto encryptprivate_keywhich is a private key str previously generated byAsymmetric.generate_keys
returns the signature text as a
str.
Example
from crypto import Asymmetric
private_key = "MIICeAIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAASCAmIwggJeAgEAAoGBAM16LLfYjbGmO67C0UZvPr5d49P2Bzh9H1Jf9aZMLAnQt9Y+88cjjfsSyxY7VQTHwySEOKvNmVKqzl0GEi8jaMzvHL3R1mjjTKAK2Q6wq/iQXCJypBOnbP0VO+ZbWiLOqe9TxF+sycSGZMbauYRTnHZ6vEKiN256k5U/DhFj68+tAgMBAAECgYA7JnqNCgfwJfx0WJzJ++hCAOE++Uom1s4XdoxOrQrYYH8ra7/dibyrlENmSPo2gBMLBg0SWANVKtpxKPg/HaBjKjMRr2vYxN0944Mw1qJlRh8qbjcn7lnxQeWSr5ygFZgVCN9PWtGrqIanNquK/hmW9RPAEd/c25wpi9wQ7XztOQJBAOtCw+dRixVqaBHalUljd0uEduMUd8jRN7kyBTtNd4ayI3ZiWlnmt4W5zhI9tQ1EjRtmMlaG0OGu/m+6Figfj6sCQQDfl0VNCgGy/S8yUtgJ6LvF6JHzP02imzvEpbPJkUzjtw/VndThG3c/i03tOCFR8232oA42CLmqdwqVZFzNsqYHAkEAkDBob1L8ApEn3aFxk/xBdmhmkUDPNaZ9F6V/rVwKYOS3dWxMYgNVAcHiei2V1N7p+RwGyB9y0I93ZDTSNZ86ZwJBAIBXIi5QWh1VeuvV5a/6aR32myAW7Ac0N6BuxL4kqw/imjIxwGneDBrraTWLDIUvx6TSxpV5eKlCX07VJvfjXa0CQQCUDfMb/Od6A28lQzGS/6bDyXaKxLA7f8nVqmCVbFt8s65x74+tSdu6thQvXojGvyvTJ33AHnwirAP2Mwh+9KZs"
hash_str = "0917b13a9091915d54b6336f45909539cce452b3661b21f386418a257883b30a"
signature = Asymmetric.sign(hash_str, private_key)
Verifying
The static method Asymmetric.verify(signature, public_key):
accepts two parameters:
signaturewhich is thestrto encryptpublic_keyis a public keystrpreviously generated byAsymmetric.generate_keys
returns the hash that was signed as a
str.
Example
from crypto import Asymmetric
signature = "dGkXV2NEog4MgqdXH+qQtiTg5j6mjbbNTHpewZ1fc2Az8Ik+ykLaA+WxLeC/4e+dhseIhNoelHz3pcwqC7mpRCuZTLJYSKumnl2wEm1ieGeQce58r34JyjgOkyKt24yY6153z+uQ4nX5IBNrjH9cMKjTG5Mn82skBSKgsbfItg4="
public_key = "MIGfMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4GNADCBiQKBgQDNeiy32I2xpjuuwtFGbz6+XePT9gc4fR9SX/WmTCwJ0LfWPvPHI437EssWO1UEx8MkhDirzZlSqs5dBhIvI2jM7xy90dZo40ygCtkOsKv4kFwicqQTp2z9FTvmW1oizqnvU8RfrMnEhmTG2rmEU5x2erxCojduepOVPw4RY+vPrQIDAQAB"
recovered_hash = Asymmetric.verify(signature, public_key)
from crypto import Asymmetric
# Generate keys
private_key, public_key = Asymmetric.generate_keys()
print("Public key:", public_key)
print("\nPrivate key:", private_key,)
# Encrypting
message = "SECRET"
ciphertext = Asymmetric.encrypt(message, public_key)
print("\nCiphertext:", ciphertext)
# Decrypting
plaintext = Asymmetric.decrypt(ciphertext, private_key)
print("\nPlaintext:", plaintext)
crypto.py
from typing import List
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.asymmetric import rsa, padding as asym_padding
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.asymmetric.utils import Prehashed
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import hashes, serialization
import base64
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
class Symmetric:
@staticmethod
def generate_key() -> str:
# Returns a Base64-encoded key as an ASCII string
return Fernet.generate_key().decode('ascii')
@staticmethod
def encrypt(message: str, key: str) -> str:
if not isinstance(message, str):
raise TypeError("message must be a string")
if not isinstance(key, str):
raise TypeError("key must be a string")
if len(message) == 0:
raise ValueError("message must not be empty")
try:
message_bytes = message.encode('ascii')
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError("Failed to encode message in ASCII") from e
try:
key_bytes = key.encode('ascii')
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError("Failed to encode key in ASCII") from e
return Fernet(key_bytes).encrypt(message_bytes).decode('ascii')
@staticmethod
def decrypt(encrypted: str, key: str) -> str:
if not isinstance(encrypted, str):
raise TypeError("encrypted must be a string")
if not isinstance(key, str):
raise TypeError("key must be a string")
try:
encrypted_bytes = encrypted.encode("ascii")
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError("Failed to encode encrypted message in ASCII") from e
try:
key_bytes = key.encode('ascii')
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError("Failed to encode key in ASCII") from e
return Fernet(key_bytes).decrypt(encrypted_bytes).decode('ascii')
class Asymmetric:
@staticmethod
def generate_keys() -> List[str]:
# Generate a new RSA key pair
private_key_obj = rsa.generate_private_key(
public_exponent=65537,
key_size=1024
)
public_key_obj = private_key_obj.public_key()
# Serialize the private key to DER format
der_private = private_key_obj.private_bytes(
encoding=serialization.Encoding.DER,
format=serialization.PrivateFormat.PKCS8,
encryption_algorithm=serialization.NoEncryption()
)
# Serialize the public key to DER format
der_public = public_key_obj.public_bytes(
encoding=serialization.Encoding.DER,
format=serialization.PublicFormat.SubjectPublicKeyInfo
)
# Encode the DER bytes into Base64 strings
b64_private = base64.b64encode(der_private).decode('utf-8')
b64_public = base64.b64encode(der_public).decode('utf-8')
return b64_private, b64_public
@staticmethod
def encrypt(message: str, public_key: str) -> str:
if not isinstance(message, str):
raise TypeError("message must be a string")
if not isinstance(public_key, str):
raise TypeError("public_key must be a string")
message_bytes = message.encode('utf-8')
# Validate and decode the Base64 public key string
try:
der_public_bytes = base64.b64decode(public_key)
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError("public_key is not valid Base64") from e
try:
loaded_public_key = serialization.load_der_public_key(der_public_bytes)
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError("Failed to load public key from DER bytes") from e
# Determine maximum allowed message length.
# The formula for RSA OAEP is: key_size_in_bytes - 2 * (hash digest size) - 2.
hash_algo = hashes.SHA256()
max_length = (loaded_public_key.key_size // 8) - 2 * hash_algo.digest_size - 2
if len(message_bytes) > max_length:
raise ValueError(
"Message too long for RSA encryption with a {}-bit key and SHA256 OAEP padding; "
"maximum is {} bytes, got {} bytes".format(
loaded_public_key.key_size, max_length, len(message_bytes)
)
)
encrypted_message = loaded_public_key.encrypt(
message_bytes,
asym_padding.OAEP(
mgf=asym_padding.MGF1(algorithm=hashes.SHA256()),
algorithm=hashes.SHA256(),
label=None
)
)
return base64.b64encode(encrypted_message).decode('utf-8')
@staticmethod
def decrypt(encrypted: str, private_key: str) -> str:
if not isinstance(encrypted, str):
raise TypeError("encrypted must be a string")
if not isinstance(private_key, str):
raise TypeError("private_key must be a string")
# Validate and decode the Base64 encrypted message string
try:
encrypted_bytes = base64.b64decode(encrypted)
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError("encrypted message is not valid Base64") from e
# Validate and decode the Base64 private key string
try:
der_private_bytes = base64.b64decode(private_key)
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError("private_key is not valid Base64") from e
try:
loaded_private_key = serialization.load_der_private_key(
der_private_bytes,
password=None
)
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError("Failed to load private key from DER bytes") from e
decrypted_bytes = loaded_private_key.decrypt(
encrypted_bytes,
asym_padding.OAEP(
mgf=asym_padding.MGF1(algorithm=hashes.SHA256()),
algorithm=hashes.SHA256(),
label=None
)
)
return decrypted_bytes.decode('utf-8')
@staticmethod
def sign(message: str, private_key: str) -> str:
"""
Signs pre-hashed data using RSA PKCS#1 v1.5 with a SHA-256 prehash.
:param message: A hexadecimal string representation of the SHA-256 hash.
:param private_key: A Base64-encoded DER private key.
:return: The Base64-encoded signature.
"""
if not isinstance(message, str):
raise TypeError("message must be a string")
if not isinstance(private_key, str):
raise TypeError("private_key must be a string")
# Convert the hex string to raw digest bytes.
try:
digest = bytes.fromhex(message)
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError("Failed to convert message from hex to bytes") from e
# Decode the Base64 private key.
try:
der_private_bytes = base64.b64decode(private_key)
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError("private_key is not valid Base64") from e
# Load the private key.
try:
loaded_private_key = serialization.load_der_private_key(
der_private_bytes,
password=None
)
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError("Failed to load private key from DER bytes") from e
# Sign the pre-hashed digest using PKCS#1 v1.5.
signature = loaded_private_key.sign(
digest,
asym_padding.PKCS1v15(),
Prehashed(hashes.SHA256())
)
return base64.b64encode(signature).decode('utf-8')
@staticmethod
def verify(signature: str, public_key: str) -> str:
"""
Recovers the hash from an RSA PKCS#1 v1.5 signature using
RSAPublicKey.recover_data_from_signature and returns it as a hex string.
:param signature: The Base64-encoded signature.
:param public_key: A Base64-encoded DER public key.
:return: The recovered hash as a hex string.
"""
if not isinstance(signature, str):
raise TypeError("signature must be a string")
if not isinstance(public_key, str):
raise TypeError("public_key must be a string")
# Decode the Base64 public key.
try:
der_public_bytes = base64.b64decode(public_key)
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError("public_key is not valid Base64") from e
# Load the public key.
try:
loaded_public_key = serialization.load_der_public_key(der_public_bytes)
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError("Failed to load public key from DER bytes") from e
# Decode the signature from Base64.
try:
signature_bytes = base64.b64decode(signature)
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError("signature is not valid Base64") from e
# Recover the padded data using recover_data_from_signature.
try:
recovered_data = loaded_public_key.recover_data_from_signature(
signature_bytes,
asym_padding.PKCS1v15(),
algorithm=hashes.SHA256()
)
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError("Failed to recover data from signature") from e
# Expected DER prefix for SHA-256 DigestInfo:
sha256_der_prefix = bytes.fromhex("3031300d060960864801650304020105000420")
if recovered_data.startswith(sha256_der_prefix):
recovered_digest = recovered_data[len(sha256_der_prefix):]
if len(recovered_digest) != 32:
raise ValueError("Recovered hash length is not 32 bytes")
return recovered_digest.hex()
elif len(recovered_data) == 32:
# Likely, the signature was created with Prehashed mode,
# so the recovered data is just the raw digest.
return recovered_data.hex()
else:
raise ValueError("Recovered data does not have the expected SHA256 DER prefix")
Code Challenge: Sign a Message
Your boss, M, has just issued a new directive at MI6. In addition to encrypting communications, every message you send must now be digitally signed. This extra layer of security ensures that the orders you receive are authentic.
Write a script that signs messages.
Note
You’ve been given a module called crypto which contains a class called Asymmetric. Use the Asymmetric class to sign the message.
Requirements
You must first hash the message using SHA-256
You must use your private key to sign the message. Your private key can be found in
private_key.txt.
Example
Enter a message: Knock, knock!
Hash:
1b674b1eae47584fc2f0d73ed466c3560a7c5830620df0c3624d89035f8e1160
Signature:
LyAbRt4qJYboDqTBVNPHl6TetfiM/KgewoauWWjXdt/309jix/BQ1a8SLO1Ppho2/uRgr9aKpmcgySGg2bydc0x9HxotGbB4xvXlmHK6jcSquvSVuscQtV6HF/6GBOtNBhc7zayM6BaMH3xeUA/IXQrg1v/i1ZE8uM9kI2m/8cQ=
MIICeAIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAASCAmIwggJeAgEAAoGBAMuI1l31tPyVOUHi7DVce/5L8ppHn5ghWdFu11qhuc15BygGi2cwpldAuh7mNmRODPhBcV6jbyfsImqb7UAAHvt9asfP8TRAYA4UP0AhqRsHo1qlPrz6lELcDTTp8W+EVgys0O/9we3hJVMYjbYTjLfjgK+FP6VskjK+gymA3ZWpAgMBAAECgYEAyiih8zWHjJGTC3Qe9Wlk5tH8p2yYgfwuQCz9zdFwwTuC9ih58gaKUYPC2coDIGG91B78QenHEDokfQte/QChw5fs5dX4mwIR51QK+c/qgUmuvSeL4ZroEfEHP4xyxSE6AZue8zkMkkOmM+vdjam5Rj5QgYbwcSMtT32g4VGR5wECQQDoIayuobOuQn7OWdT4HTUrgRNCSeNKvB/GSXfbaosxTWFHgsSYWeTsc6jG3g+bkPjFHIXRsfTny122zlz2Mnn5AkEA4HZpl+nWDwpWsEC+/WNWoKWLL7tfS72gdySt2pTi6JfBnAgZkqJUSotsuUUE1aKBEaty8I8Myni3fcRETP1lMQJBAIGfbEIH4cIJN64a06XJCYvFg++cOuPcsRGUrO1FTXy2bP/1sboxWHgBDdoe3jBMf93x03gJG2zkTuxpx9di0GECQQCq3JhOgjpmookQi4iW22pSyRDlWa0Vu5gNeYc5jwIW6YYAXw4QV67wO6ecdBRVBulW6PqKcWncKf4LJz6SmITRAkBxsFhEWgCSpLWDnuZykOSY5xyVWPfQ5O9x8lS5ygyIkG7b8AjEHXwMcBcdcCFvwlTf8Cj8cX9I1jdutHBgk6PT
Solution
Solution is locked
Code Challenge: Verify a Message
You’ve received new instructions from M but before you act, you must ensure it’s authentic.
Write a script that verifies messages.
Note
You’ve been given a module called crypto which contains a class called Asymmetric. Use the Asymmetric class to verify the message.
Requirements
You must use M’s public key (below)
The message has been hashed using SHA-256
If the hashes match, show the success message
Public Key
M’s public key is
MIGfMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4GNADCBiQKBgQDAq7KiIoE9L5v2KSX+NvFG0FMzeA7AMdemTN0I7TXp+hQdNJ2GQ58x+qpTdg92nPzfsn5b2OFHYU2ztbBsVC0FPmjU+OKv1yb0ps08fRFN3NHJZXIwR89S+kzULShP+OJlk4IBYWAwb4V6pOKugxGqWE6fLSh7HJMTfEpBYQsyKwIDAQAB
Example
Enter a message: Knock, knock!
Enter the signature: CRLb+XybnkpxcYk3RqOndnjRW+J/FExRn4Ye5yZHzq/ZwU3aI0zLUl9eru5Hq8BLgkGiTcqqbTOnp1HqnkzLfYilaPkkmOn8vtkp+EnEqRXfIAXmi+v6W0AkBMPxYoLavWqmvZQUMI96yNOTPq/YqNMq0SAm+m3yfHbiR29ewlg=
Hash:
1b674b1eae47584fc2f0d73ed466c3560a7c5830620df0c3624d89035f8e1160
Recovered Hash:
1b674b1eae47584fc2f0d73ed466c3560a7c5830620df0c3624d89035f8e1160
SUCCESS: Hashes match!
Solution
Solution is locked