Stack#
Stacks are LIFO data structures, meaning that we can only access the most recently placed (pushed) item onto the stack.
This makes them a natural fit to be implemented by a linked list, because
we only need to modify the head of a linked list for this operation, which
has time complexity of O(1). No matter how tall the stack becomes, it always
takes the same, small constant amount of time to push or pop.
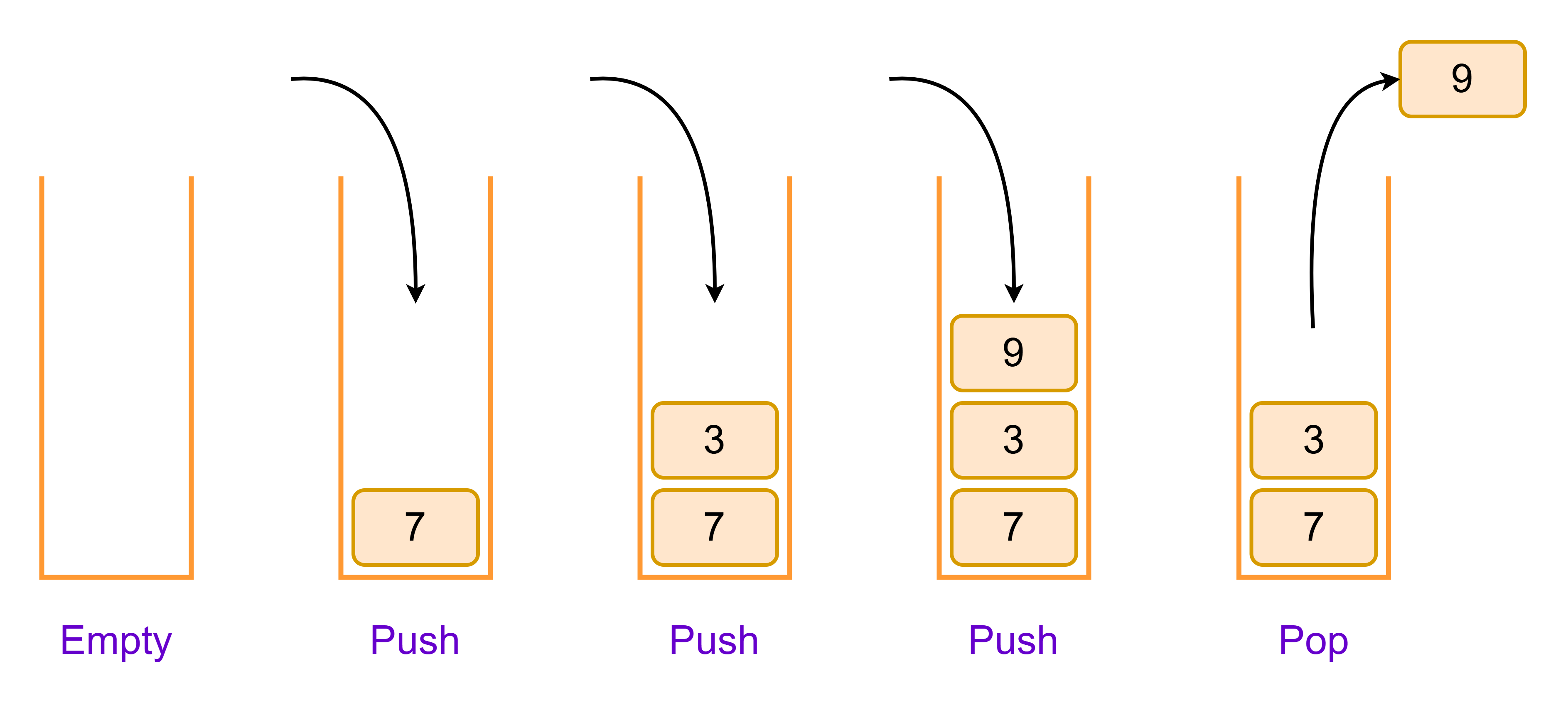
Push#
Pushing to a stack is the same operation as prepending to a linked list. The push operation can be summarised as:
Create a new node with the
dataandnext = headSet the
headof the linked list to the new node
Each push operation extends the linked list underneath the
Pop#
Popping a stack is the reverse operation of pushing. We need to undo the most recent push by:
Checking if there’s any elements on the stack
Save a copy of the current
headdataSet the
headof the linked list to the next nodeReturn the saved copy of the old head data
Code Challenge: Stack
Using your Node class from from the Nodes example, complete the provided Stack class.
Stack Specifications
Attributes
head, a reference to the top of the stack
Methods
pop(self), removes and returns the element at the top of the stackpush(self, data), adds an element to the top of the stack
Instructions
Note
Look for the TODO items in the provided code!
Copy and paste the
Nodeimplementation from the previous exercise to the top of the scriptComplete the
pushmethod:Create a new node with the
dataandnext = headSet the
headof the linked list to the new node
Complete the
appendmethod:Checking if there’s any elements on the stack
Save a copy of the current head data
Set the head of the linked list to the next node
Return the saved copy of the old head data
Otherwise return None
Usage Example
>>> names = Stack()
>>> names.push("Bill Gates")
>>> names.push("Steve Jobs")
>>> print(names.pop())
Steve Jobs
Here is some code for you to start with:
class Node:
# TODO: Add your Node class implementation here
# Stack definition here
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def push(self, data):
# TODO
def pop(self):
# TODO
# Test code
names = Stack()
names.push("Turnbull")
names.push("Morrison")
names.push("Albanese")
print(names.pop())
print(names.pop())
Solution
Solution is locked