5.10. Building a Neural Network For Classification#
For this example we’ll use our pass/fail dataset. A 1 means the student passed
the exam, and a 0 means they failed. pass_fail.csv.
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_csv("pass_fail.csv")
print(data)
Output
Time Spent Studying (hours) Exam Result
0 4.5 1
1 8.0 1
2 1.5 0
3 3.5 1
4 5.5 1
5 3.0 0
6 6.5 1
Building a neural network for classification is very similar to building a
neural network regression, the main differences is that instead of importing
MLPRegressor we use MLPClassifier.
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
Then when we make predictions, we can get the raw class predictions using
.predict or we can obtain the probabilities using .predict_proba.
Here is a complete example.
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data = pd.read_csv("pass_fail.csv")
x = data[["Time Spent Studying (hours)"]].to_numpy()
y = data["Exam Result"].to_numpy()
nn = MLPClassifier(
hidden_layer_sizes=(2), max_iter=500, learning_rate_init=0.1, random_state=0
)
nn.fit(x, y)
x_test = np.array([[0], [3], [5]])
print(nn.predict_proba(x_test).round(4)) # Round to 4 decimal places
print(nn.predict(x_test))
Output
[[1. 0. ]
[0.9839 0.0161]
[0. 1. ]]
[0 0 1]
Let’s interpret the outputs.
The 3 test samples we provide are of students who have studied 0 hours, 3 hours and 5 hours respectively. The output probabilities are:
[[1. 0. ]
[0.9839 0.0161]
[0. 1. ]]
[0 0 1]
Here is a summary of what this means:
Student 1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
Studetn 2 |
3 |
0.9839 |
0.0161 |
Student 3 |
5 |
0 |
1 |
Based on these probabilities students 1 and 2 are predicted to fail and student 3 is predicted to pass. This corresponds to the predictions we see:
[0 0 1]
Student 1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
Student 2 |
3 |
0.9839 |
0.0161 |
0 |
Student 3 |
5 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
Code Example: Neural Network for Classification
We’ll use a smaller version of the MNIST dataset that only contains digits 1, 2 and 3. Your tasks is to build a KNN classification model and to use it to classify the 6 samples provided in the test dataset. These images are provided below.
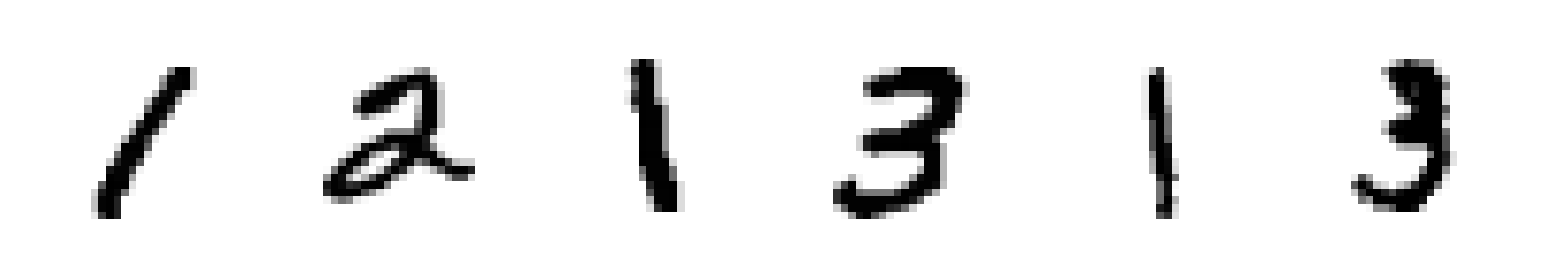
Note
Each image in the dataset has been flatted into a single row of pixels. For more details and examples refer to Extension: Image Data. from lesson “4. K-Nearest Neighbours and K-Means Clustering”
Instructions
Using pandas, read the files
123_xtrain.csv,123_ytrain.csvand123_xtest.csvintoDataFramesand then convert them to numpy arrays.Reshape the y training values using
.reshape(-1, )(this turns the y values into a 1D array)Using
sklearn.neural_network, create aMLPClassifierThe neural network should have 3 hidden layers with 10, 20 and 10 neurons in these layers
Set the maximum number of iterations to 500
Set the learning rate to 0.001
Set
random_stateto 0
Fit the data neural network to the training data
Obtain the prediction probabilities of the test data, round this to 3 decimal places and print the results
Print the predicted the class labels
Your output should look like this:
[[X. X. X.]
[X.XXX X.XXX X.XXX]
[X. X.XXX X.XXX]
[X.XXX X.XXX X.XXX]
[X. X. X. ]
[X. X. X. ]]
[X X X X X X]
Solution
Solution is locked
Extension More Training
We have provided a larger training set for you to work with locally. Use this to try to build a better neural network. Things to consider:
The size of the network
The number of iterations
The learning rate
TIPS:
Start small and build up! If you start with a huge neural network it will take a long time to train so you will be slow to make improvements. We recommend starting with something small and continuously tweaking it to improve performance.
You may also want to consider writing a script to test a whole range of different hyperparameters (e.g different network sizes) and storing the results. That way you can leave experiments running over night and check the results in the morning.
Don’t forget that what we care about is how well the neural network does on unseen data. You might want to withhold some of the training data as validation data so you can see how well the model does on new data.