1.3. Linear Regression#
Linear regression is a commonly used machine learning algorithm. It is:
A form of supervised learning (data is labelled)
A regression algorithm (predict a number)
The way it works is that the computer is given some data, and then the computer will fit a line to the given data. Based on the given line, the computer will try to make predictions on new data.
Consider the following dataset:
Time Spent Studying (hours) |
Exam Mark (%) |
|---|---|
4.5 |
60 |
8 |
80 |
1.5 |
31 |
3.5 |
54 |
5.5 |
58 |
3 |
30 |
6.5 |
78 |
We can plot this data out on a graph as shown below:
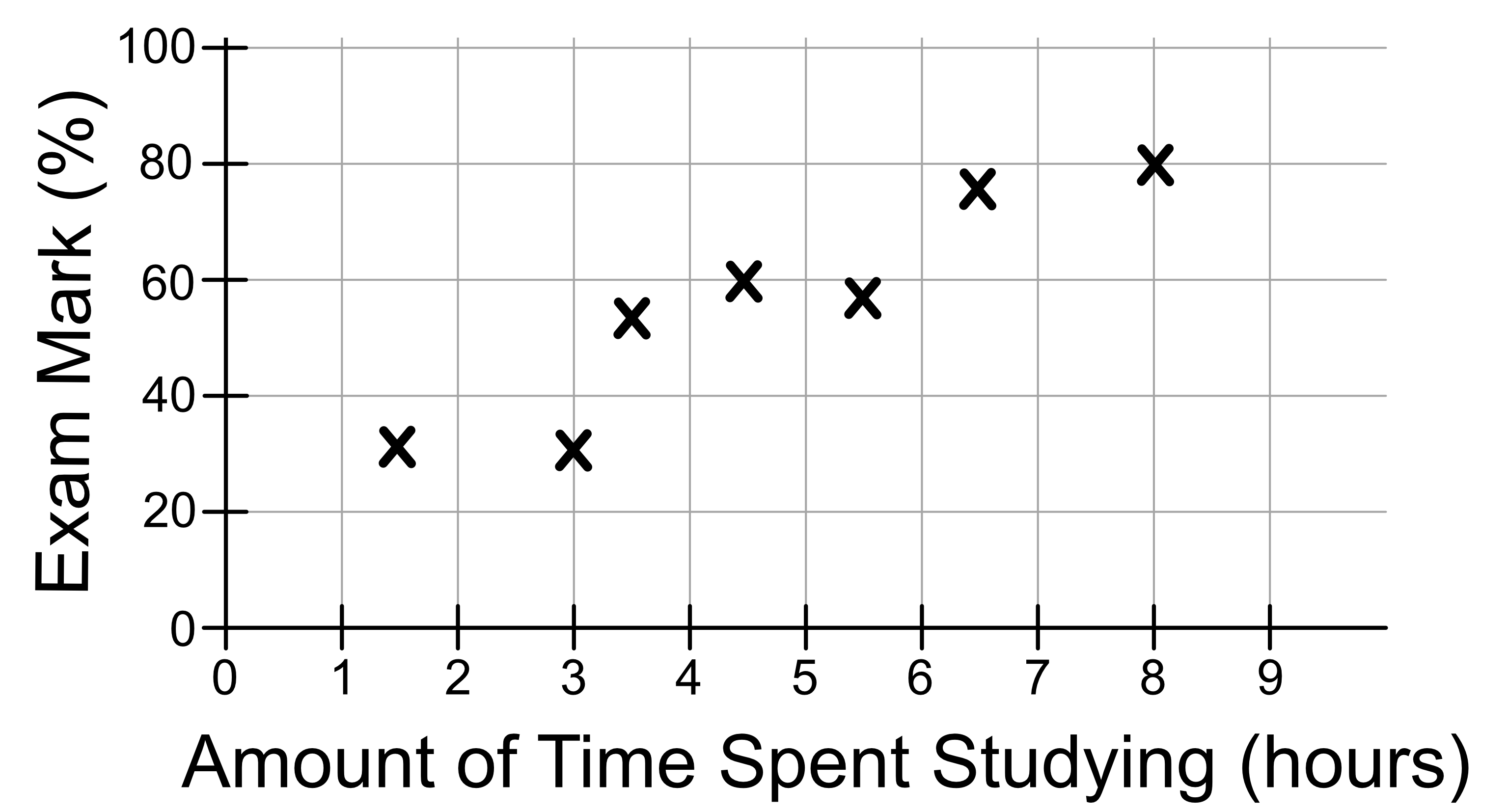
We then fit a line to the data. We call this line our model.
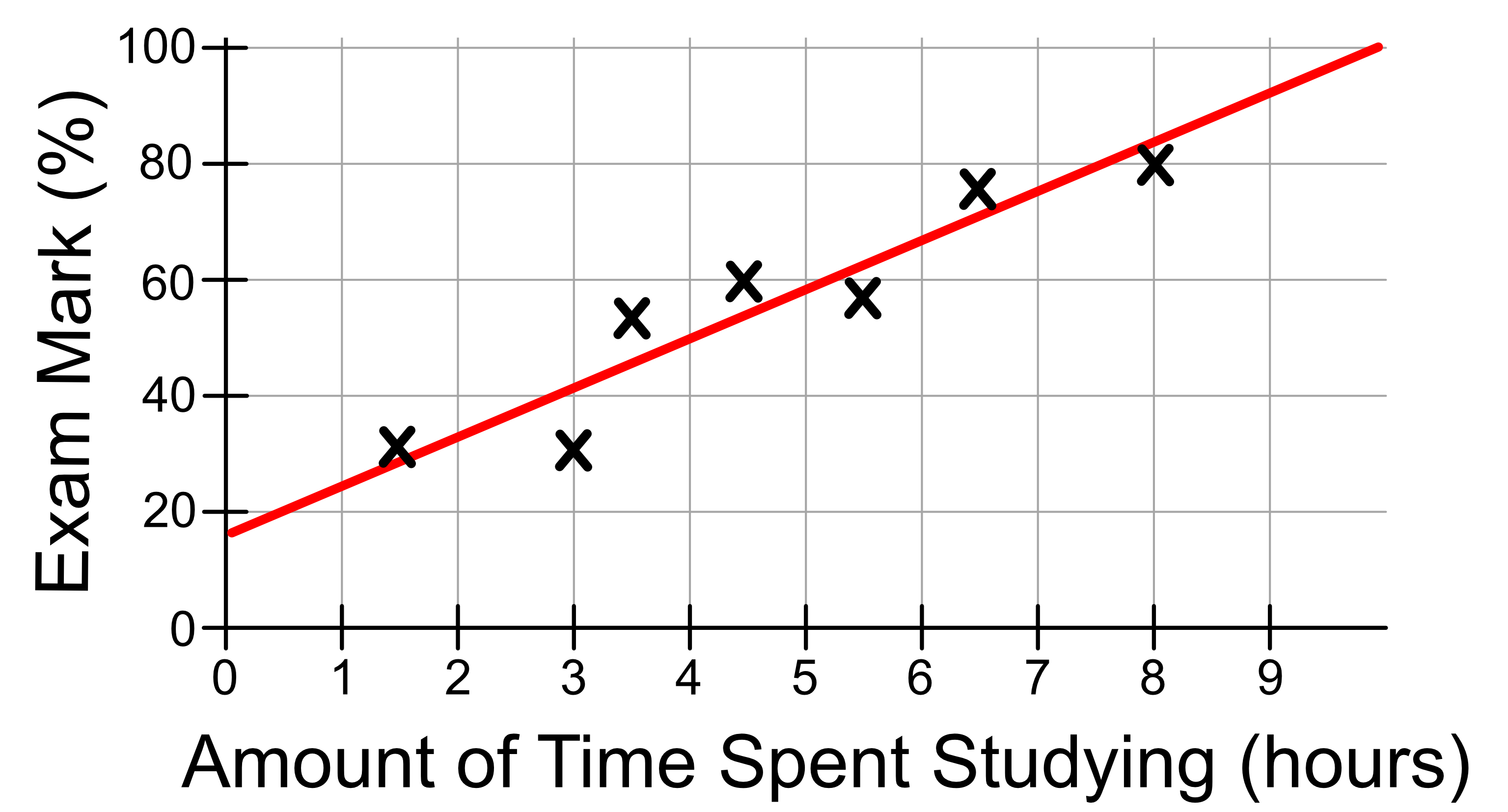
Our model can be described using the mathematical equation for a line.
where \(\beta_0\) is the intercept of our line, which in this case is 17 and \(\beta_1\) is the gradient (rise divided by run) of our line, which in this case is approximately 8. \(x\) is our independent variable, the amount of time spent studying and \(y\) is our dependent variable, the exam mark. Therefore our model is:
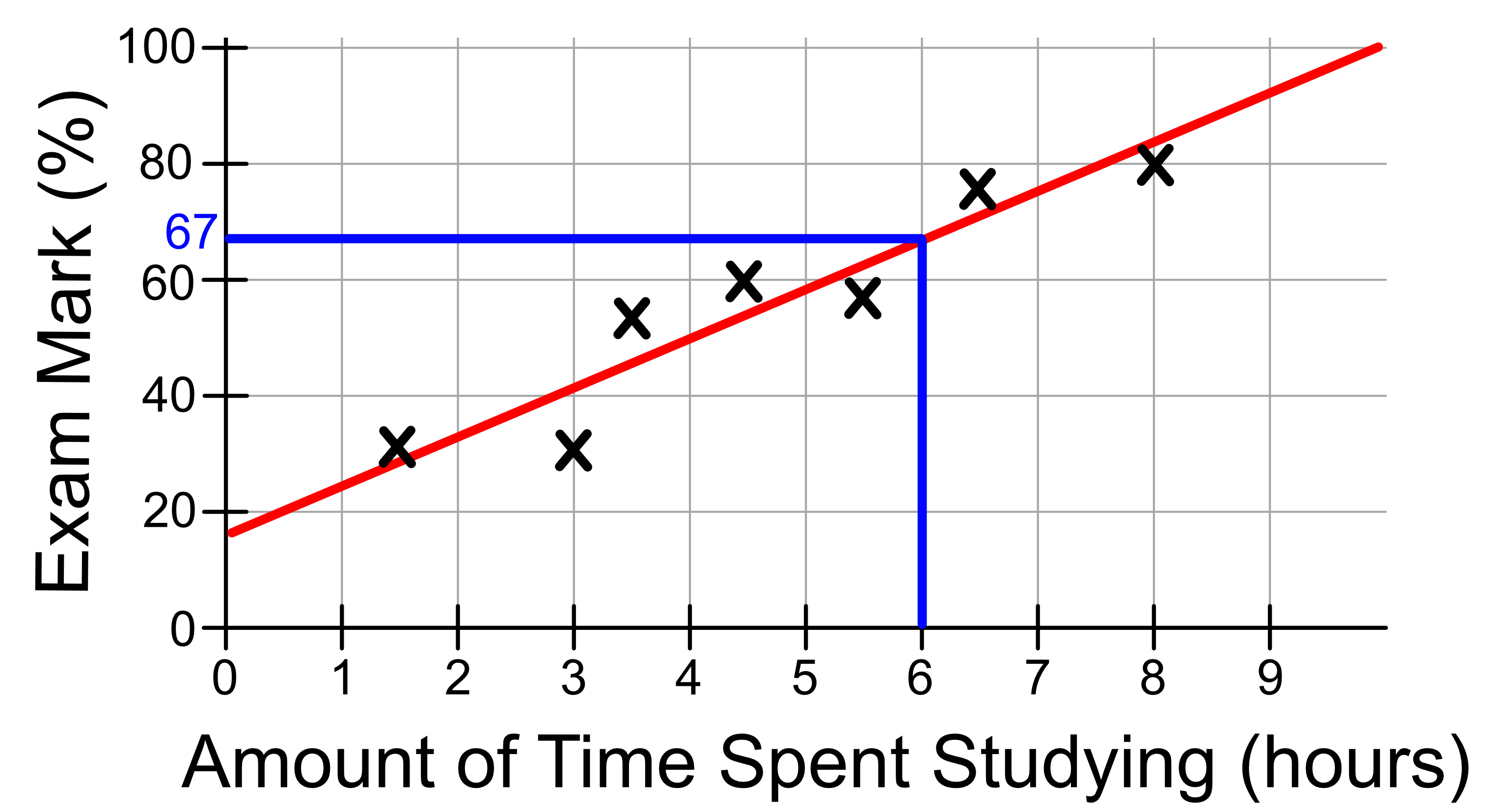
Using our model we can make predictions. For example, let’s estimate the mark of a student who has studied 6 hours for the exam. Using our model formula and plugging in \(x=6\), gives us:
This means that we predict a student who has studied 6 hours for the exam will get a mark of 67. We can also estimate this number from the graph directly.