7.1. Types Of Machine Learning Summary#
Machine learning models typically fall into four types of learning: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning and reinforcement learning.
7.1.1. Supervised Learning#
Supervised learning is when the model is trained using a labelled dataset, i.e. you are given data with known input(s) and as well as known output(s).
Examples of supervised learning algorithms include: linear regression, polynomial regression, logistic regression, decision trees (for regression and classification), k-nearest neighbours (for regression and classification) and neural networks.
7.1.2. Unsupervised Learning#
Unsupervised learning is what the model is trained using an unlabelled dataset. The goal of the model is to find patterns or structures in the data on it’s own.
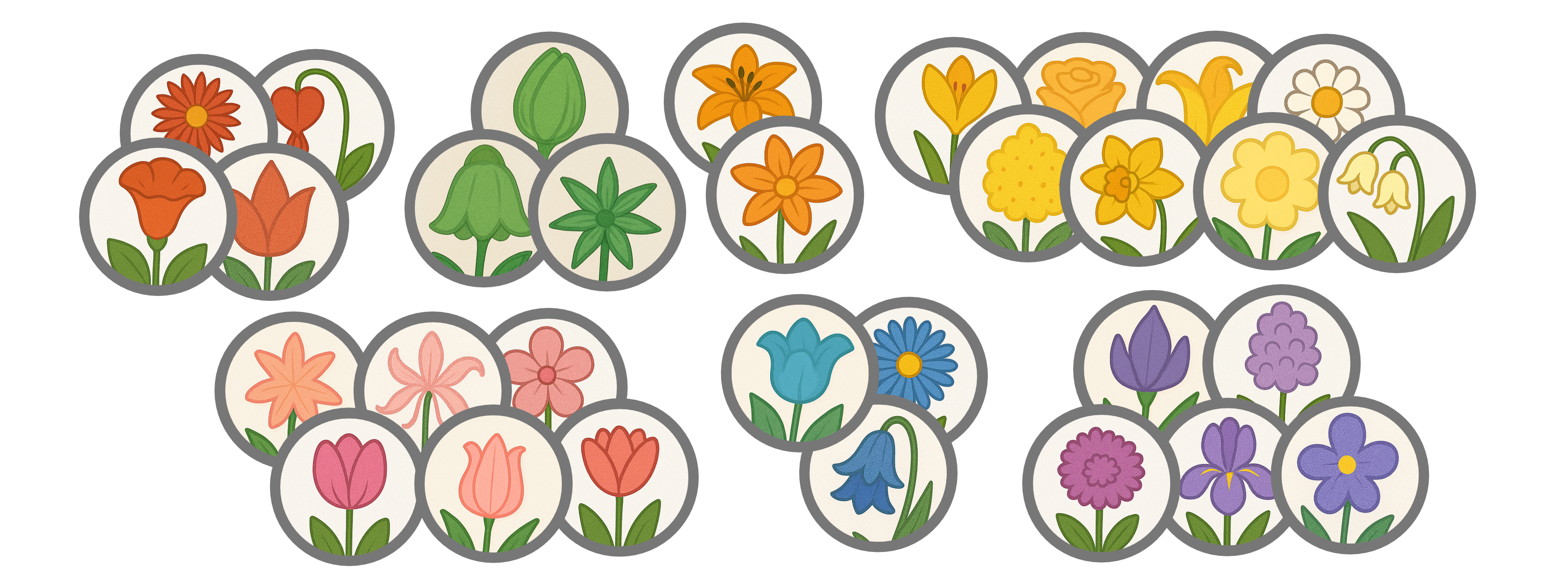

An example of an unsupervised learning algorithm is k-means clustering.
7.1.3. Semi-supervised Learning#
Semi-supervised learning involves training a model using a mix of labeled and unlabelled data. It’s particularly useful when labeled data is scarce or expensive to obtain. A common approach starts by training a supervised model on the available labeled data. This model is then used to generate predictions on the unlabelled data, which serve as pseudo-labels. Only the samples where predictions were made with high confidence are typically selected and treated as if they were true labels. These pseudo-labeled examples are added to the training set to expand it, with the aim of improving the model’s overall performance by leveraging more data.
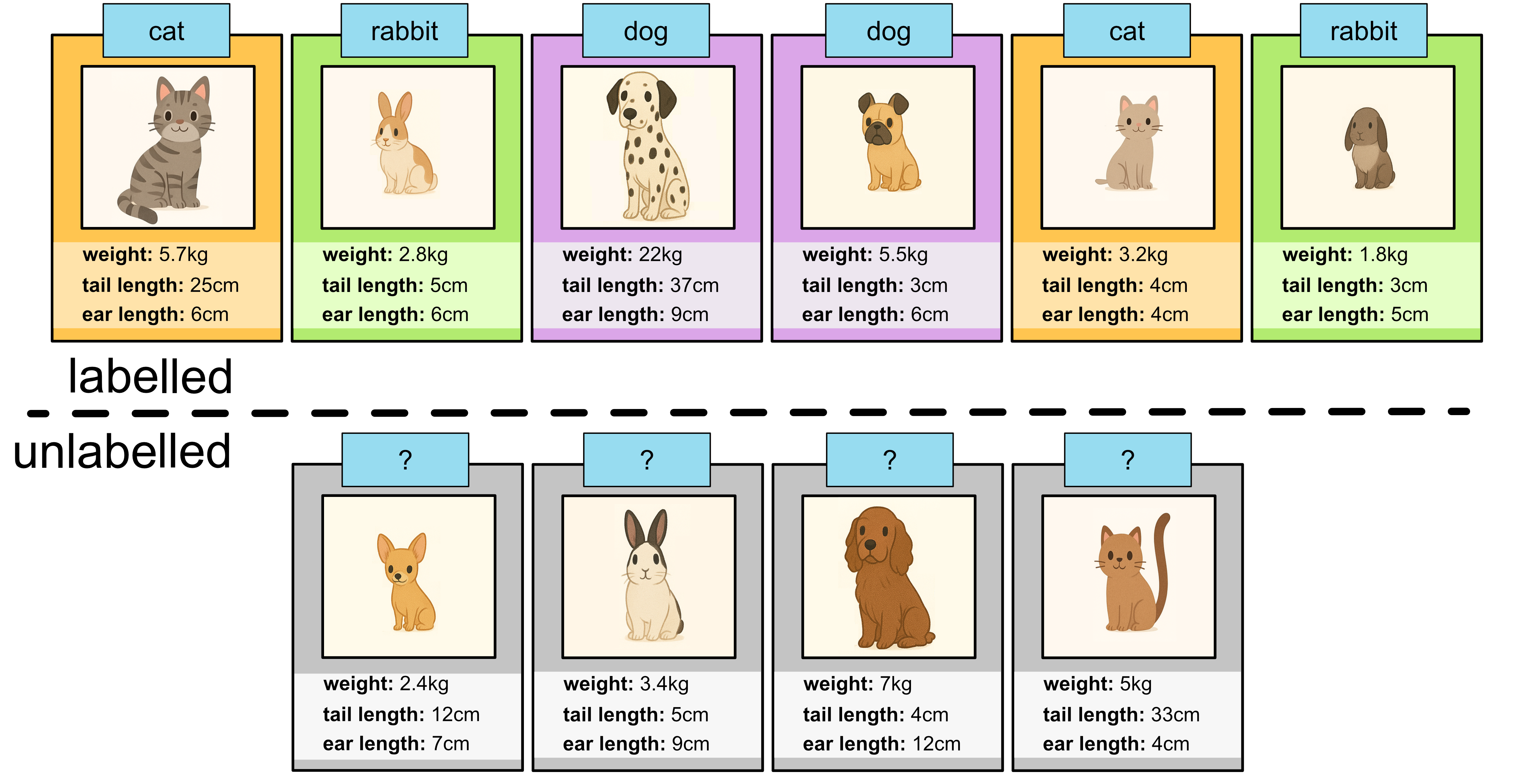
All the supervised learning algorithms listed earlier can be trained using a semi-supervised approach.
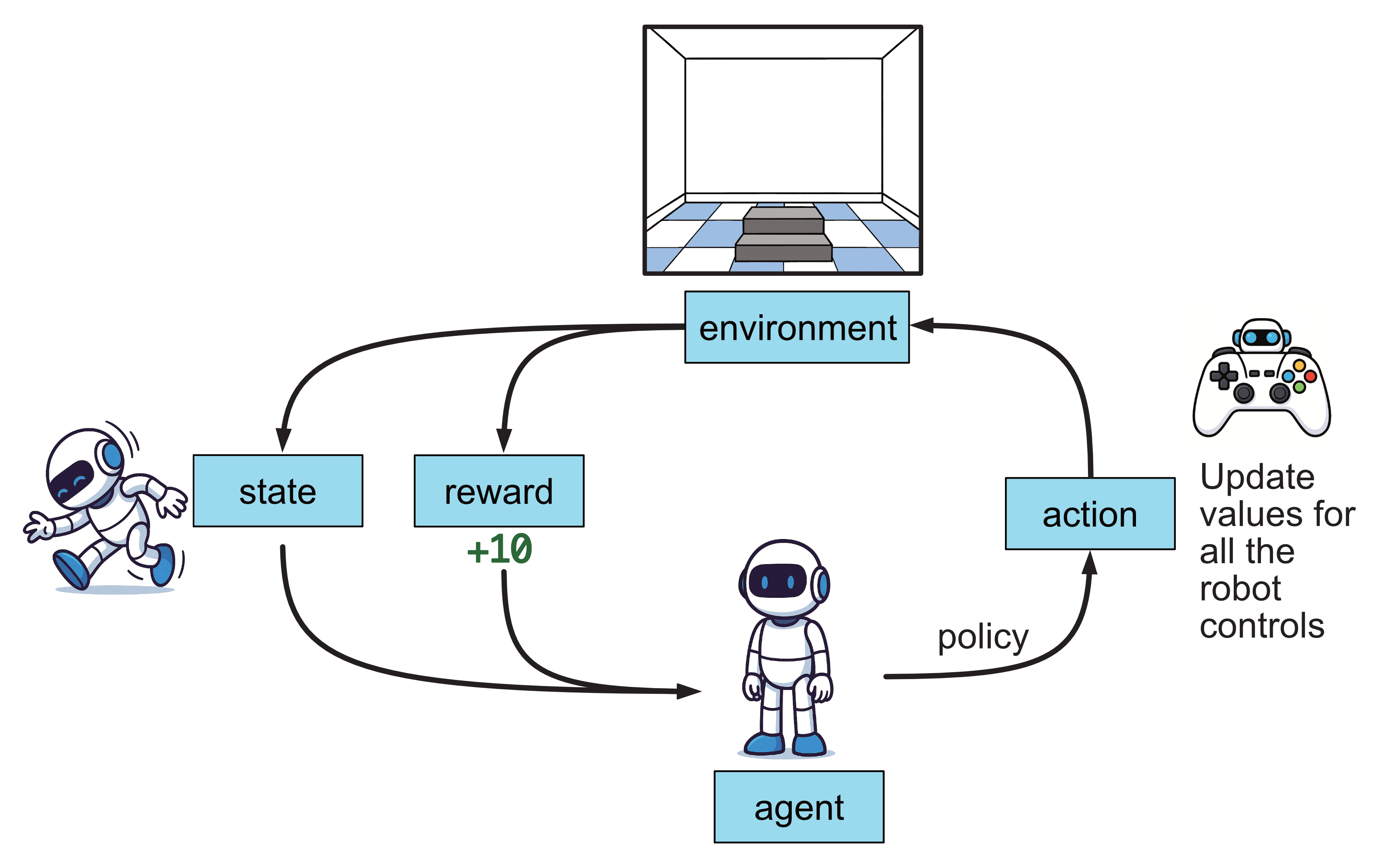
7.1.4. Reinforcement Learning#
Reinforcement learning is a type of machine learning where an agent learns to make decisions by interacting with an environment. The agent takes actions, receives rewards (or penalties), and uses this feedback to improve its behaviour over time. The goal is to learn a policy, which is a strategy for choosing actions, that maximises the total reward. Through trial and error, the agent gradually figures out what actions lead to better outcomes.